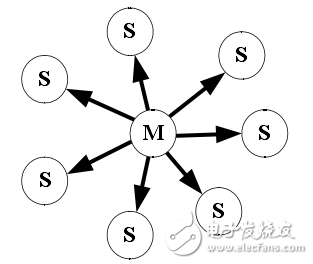
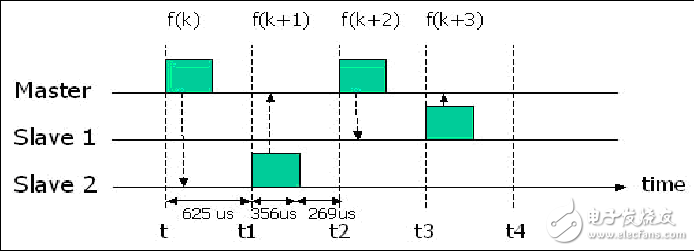
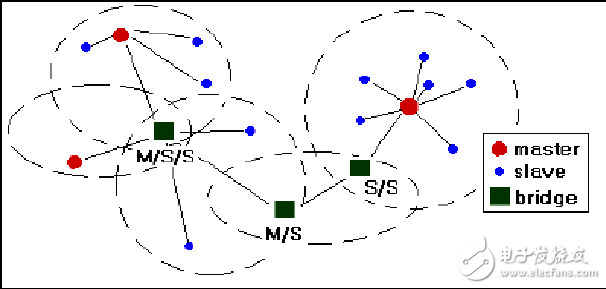
As a small-scale wireless connection technology, Bluetooth technology can realize convenient, fast, flexible, low-cost, low-power data and voice communication between devices. It is one of the mainstream technologies for implementing wireless personal area network. At the same time, the Bluetooth system works in the way of Ad Hoc, and each Bluetooth device can implement the routing function in the network, which can form a mobile ad hoc network. The characteristics of Bluetooth fit the Ad Hoc and WPAN concepts in many ways, showing its true potential. Moreover, connecting Bluetooth to other networks can lead to a wider range of applications, such as access to the Internet, PSTN or public mobile communication networks, which can make user applications more convenient or bring greater benefits to users. As a supplement to the hospital's wired LAN, the Bluetooth wireless personal area network overcomes the drawbacks of the wired network, and can use the computer to perform the query and input of vital signs data anytime and anywhere, and plays an important role in wireless monitoring. 1 Bluetooth networking mechanism 1.1 Network characteristics of Bluetooth personal area network As a working group of the Bluetooth SIG, the main goal of the Bluetooth Personal Area Network Working Group is to define an IP-based Bluetooth personal area network application protocol, to address the encapsulation of Ethernet data packets, IP-based personal area networks, and master devices in a single piconet. Forwarding and problems with LAN access points. The Bluetooth Personal Area Network protocol describes how two or more Bluetooth devices form an Ad Hoc network and how to access the remote network through a network access point using the same mechanism. A network access point can be a traditional LAN data access point, while a packetized Ad Hoc network represents only a set of interconnected devices. A packetized Ad Hoc network is a collection of mobile hosts that can be combined to form an Ad Hoc wireless network without the support of other network hardware or network facilities. The PAN protocol is more focused on a simple personal Ad Hoc network consisting of a Bluetooth piconet. There are up to 8 devices in the network, one of which is the master node and the rest are slave nodes. The Bluetooth PAN network has the following common features of the Ad Hoc network: (1) Independent networking capabilities With the support of certain network composition algorithms, each node can automatically form an independent network in a short period of time without any network infrastructure support. (2) Multi-hop routing The node's transmit power is low, so coverage is limited. Node communication outside the range of mutual communication needs to be forwarded by the intermediate node and implemented through multiple hops. (3) Topological dynamic changes In Bluetooth PAN, some nodes are mobile, may leave or rejoin the network at any time, and some nodes may turn off the power at any time, causing changes in the distribution of nodes and links. Therefore, the topology of the Bluetooth PAN may change at any time. (Special channel characteristics The impact of the wireless channel conflict, signal attenuation, noise and interference between the channels, the actual bandwidth of the Bluetooth link is much smaller than the theoretical bandwidth, and dynamic changes. (5) Limitations of nodes Most Bluetooth nodes rely on battery power, energy is limited, and nodes have mobility, small memory and limited processor processing capacity, so it is very important to effectively reduce node energy consumption. (6) Security Although Bluetooth adopts a strict security mechanism, due to the characteristics of the Ad Hoc network, the Bluetooth node is vulnerable to network attacks such as eavesdropping, active intrusion and denial of service. Bluetooth PAN also has some features that are different from other Ad Hoc networks: (1) Limited communication range of nodes The effective transmission distance of the Bluetooth node is generally several meters to several tens of meters, and the self-organizing network such as IEEE802.11 can reach several hundred meters. (2) Relatively small mobility Bluetooth nodes move at a lower speed and frequency than other Ad Hoc network devices. (3) narrow bandwidth Bluetooth is usually used for applications such as data, voice and low-rate video transmission. Therefore, the bandwidth is narrow. The maximum bandwidth defined by the Bluetooth 2.0 specification is only 3 Mbit/s. Therefore, the optimization of Bluetooth network bandwidth is an important development direction. 1.2 Bluetooth network topology The Bluetooth system uses a flexible baseless networking method that allows one Bluetooth device to connect to seven other Bluetooth devices. The topology of the network structure of the Bluetooth system has two forms: a piconet and a scatternet. (1) piconet A piconet is a micro-network that is connected in a specific way through Bluetooth technology. A piconet can be just two connected devices, such as a laptop computer and a mobile phone, or eight connected devices. In a piconet, all devices have the same level and have the same permissions. Bluetooth adopts Ad Hoc, consisting of a master device (master-initiated device) and a slave device (Slave), with one master device unit and up to seven slave device units, such as Figure 1 shows. The master unit is responsible for providing a clock synchronization signal and a frequency hopping sequence, and the slave unit is typically a controlled synchronized equipment unit that is controlled by the master unit. Figure 1 A master device and a piconet of up to seven slave devices In each piconet, a set of pseudo-random hopping sequences is used to determine 79 hopping channels. This hopping sequence is unique to each piconet and is determined by the address and clock of the master node. The Bluetooth wireless channel uses a frequency hopping/time division multiplexing (FH/TDD) scheme, and the channel divides the time slots by a length of 625 μs. The time slots are numbered according to the clock of the primary node of the piconet, and the number is from 0-(227-1) to 227. For a loop length, each time slot corresponds to a frequency hopping frequency, and the frequency hopping rate is usually 1600 hops/s. The master node only transmits information at even time slots, the slave node only starts transmitting at odd time slots, and the beginning of the packet corresponds to the beginning of the time slot. The characteristics of the channel in the piconet are completely determined by the master node. The Bluetooth address (BD_ADDR) of the master node determines the frequency hopping sequence and the channel access code, and the system clock of the master node determines the phase and time of the frequency hopping sequence. According to the equality of the Bluetooth nodes, any device can become the master node in the network, and the master and slave nodes can convert roles. The master node communicates between the two by polling the slave node. The slave node can only send data if it receives the packet of the master node. As shown in Fig. 2, the slave node 2 receives the data packet from the master node at time t, and the frequency is f(k), after which it can send the data packet to the master node through the f(k+1) frequency in the next time slot. Similarly, the slave node 1 receives the data packet of the master node at time t2, at which time the frequency is f(k+2), and at time t3, the data packet is transmitted to the master node by the frequency f(k+3). Figure 2 Pico network communication polling mechanism (2) Scattering network A piconet can only have up to 7 slave nodes in communication state at the same time. In order to accommodate more Device, and expand the network communication range, multiple piconets are interconnected to form a Bluetooth self-organizing network. That is, the scattering net, Figure 3. In the scatter network, different hopping sequences are used between different piconets. Therefore, as long as there is no simultaneous jump to the same channel, even if multiple sets of data streams are transmitted simultaneously, no interference will occur. The role of the serial device connected between the piconets is called a bridge. The bridge node can be the slave role in all the piconets to which it belongs. The type of the bridge is Slave/Slave (S/S); it can also be the master in one of the piconets to which it belongs, and the slave in other piconets. Such a Bridge category is Master/Slave (M/S). The bridge node realizes data transmission between the piconets through the conversion of different time slots between different piconets. The unique networking mode of Bluetooth gives the bridge node a strong vitality, and there are 7 mobile Bluetooth users connected to the Internet through a network node. It identifies each piconet by frequency hopping sequence, and all users of the same piconet are synchronized with this frequency hopping sequence. Bluetooth scatternet is a special case of ad hoc networks. Its biggest feature is that it can be supported without base stations. The status of each mobile terminal is equal, and the decision of packet forwarding can be independently performed. The characteristics of network construction flexibility, multi-hopping, dynamic topology change and distributed control are built. The basis of the Bluetooth scatternet. Figure 3 Bluetooth scattering network example
Coupletech Co., Ltd, could supply CW Laser models for medical instruments and scientific research, Q-Switched Pulse Laser models, NPLP-SEED Laser Head (Laser head), Diode-pumped pulsed Laser and Athermal Diode-pumped Pulsed Laser. e.g. UV laser, Low noise blue laser, Signal mode green laser, Sodium Yellow Laser, Light yellow Laser, Orange yellow laser, Infrared laser, Mid-infrared laser, Eye-safety Laser, Deep UV laser, 900ps-laser head, Diode-pumped Pulsed Laser without temperature control. Coupletech's laser have advantage with small volume, low weight and high reliability.
Coupletech Co., Ltd. has the R&D, Engineering, and Production expertise to manufacture lasers that are able to maintain integrity in various extreme settings and conditions. Coupletech offers diversity of laser sources for a broad range of commercial and scientific applications. We specialize in designing and manufacturing custom-made and OEM lasers to suit our clients' particular needs.
Laser Distance Measuring,Pulse Laser,Laser Diode Specifications,Yellow Laser,CW Laser,Solid-state laser Coupletech Co., Ltd. , https://www.coupletech.com