Comprehensively explain the choice of hardware firewall A firewall refers to a combination of a series of components installed between different networks (such as a trusted intranet and an untrusted public network) or a network security domain. It is the only entry and exit of information between different networks or network security domains. By monitoring, restricting, and changing the data flow across the firewall, it shields the information, structure, and operating conditions inside the network as much as possible from the outside, and selectively accepts external access. Strengthen internal device supervision, control access to servers and external networks, and build a barrier between the protected network and the external network to prevent unpredictable and potentially damaging intrusions. There are two types of firewalls, hardware firewalls and software firewalls. They can both play a protective role and filter out attackers on the network. Here I will mainly introduce you to the common hardware firewalls in the practical application of corporate network security. 1. Basic principles of firewall 1. Firewall technology The security control methods commonly used by firewalls mainly include packet filtering, status detection, and proxy services. Below, we will introduce the working mechanism and characteristics of these methods, and introduce some mainstream firewall products. The packet filtering technology is a simple and effective security control technology. It loads the data passing through the device by loading and prohibiting rules from certain specific source addresses, destination addresses, and TCP port numbers on the devices connected to each other on the network. Packets are checked to restrict data packets to and from the internal network. The biggest advantage of packet filtering is transparent to users and high transmission performance. However, because the security control layer is at the network layer and the transport layer, the security control is limited to the source address, destination address and port number, so only a preliminary security control can be carried out. For malicious congestion attacks, memory overlay attacks or viruses, etc. High-level attack methods are powerless. State detection is a more effective security control method than packet filtering. For newly created application connections, the status check checks the pre-set security rules, allows connections that meet the rules to pass, and records relevant information about the connection in memory to generate a status table. Subsequent data packets for this connection can pass as long as they conform to the state table. The advantage of this method is that, because there is no need to check the rules of each data packet, but the subsequent data packets of a connection (usually a large number of data packets) through the hash algorithm, directly check the status, so that performance is Significantly improved; moreover, because the state table is dynamic, it is possible to open ports above 1024 selectively and dynamically, so that the security is further improved. 2. How the firewall works (1) Packet filtering firewall Packet filtering firewalls are generally implemented on routers to filter user-defined content, such as IP addresses. The working principle of the packet filtering firewall is: the system checks the data packets at the network layer, regardless of the application layer. In this way, the system has good transmission performance and strong scalability. However, the security of the packet filtering firewall has certain flaws, because the system is not aware of the application layer information, that is, the firewall does not understand the content of the communication, so it may be attacked by hackers. (2) Application gateway firewall The application gateway firewall checks all the application layer packets and puts the checked content information into the decision-making process, thereby improving the security of the network. However, the application gateway firewall is implemented by breaking the client / server model. Each client / server communication requires two connections: one from the client to the firewall, and the other from the firewall to the server. In addition, each agent requires a different application process, or a service program running in the background. For each new application, a service program for this application must be added, otherwise the service cannot be used. Therefore, the application gateway firewall has the disadvantage of poor scalability. (figure 2) (3) Status detection firewall The state inspection firewall basically maintains the advantages of a simple packet filtering firewall, with better performance, and is transparent to applications. On this basis, the security has been greatly improved. This firewall abandons simple packet filtering. The firewall only examines the data packets entering and leaving the network, and does not care about the shortcomings of the packet status. It establishes a state connection table at the core of the firewall, maintains the connection, and treats data entering and leaving the network as events deal with. It can be said that the state inspection packet filtering firewall regulates the network layer and transport layer behavior, while the application proxy firewall regulates the behavior on a specific application protocol. (image 3) (4) Composite firewall The composite firewall refers to a new generation of firewall that combines status detection and transparent proxy. It is further based on the ASIC architecture and integrates antivirus and content filtering into the firewall. It also includes VPN and IDS functions. Multiple units are integrated into one. A new breakthrough. Conventional firewalls cannot prevent attacks that are hidden in network traffic. Scanning the application layer on the network interface combines antivirus, content filtering and firewalls, which reflects the new ideas of network and information security. It implements OSI layer 7 content scanning at the network boundary, and implements real-time application layer service measures such as virus protection and content filtering at the network edge. (Figure 4) 3. Comparison of four types of firewalls Packet filtering firewall: The packet filtering firewall does not check the data area, and the packet filtering firewall does not establish a connection status table. The front and rear packets are irrelevant, and the application layer control is weak. Application gateway firewall: Does not check the IP and TCP headers, does not establish a connection status table, and the network layer protection is weak. Status detection firewall: It does not check the data area, establishes a connection status table, the front and back packets are related, and the application layer control is very weak. Compound firewall: It can check the entire packet content, establish a connection status table as needed, strong protection at the network layer, fine control at the application layer, and weak session control. 4. Firewall terms Gateway: A system that provides forwarding services between two devices. A gateway is a firewall for Internet applications to process traffic between two hosts. This term is very common. DMZ demilitarized zone: In order to facilitate configuration management, the servers that need to provide services in the internal network are often placed in a separate network segment. This network segment is the demilitarized zone. The firewall is generally equipped with three network cards, which are generally respectively connected to the internal network, internet and DMZ during configuration. Throughput: The data in the network is composed of individual packets, and the firewall consumes resources to process each packet. Throughput refers to the number of data packets that pass through the firewall per unit time without packet loss. This is an important indicator for measuring firewall performance. Maximum connections: Like throughput, the higher the number, the better. However, the maximum number of connections is closer to the actual network situation. Most connections in the network refer to a virtual channel established. The firewall's processing of each connection also consumes resources, so the maximum number of connections becomes an indicator of the firewall's ability in this regard. Packet forwarding rate: Refers to the speed at which the firewall processes data traffic when all security rules are configured correctly. SSL: SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) is a set of Internet data security protocols developed by Netscape. The current version is 3.0. It has been widely used for identity authentication and encrypted data transmission between Web browsers and servers. The SSL protocol is located between the TCP / IP protocol and various application layer protocols to provide security support for data communication. Network address translation: Network address translation (NAT) is a technology that maps one IP address domain to another IP address domain to provide transparent routing for end hosts. NAT includes static network address translation, dynamic network address translation, network address and port translation, dynamic network address and port translation, port mapping, and so on. NAT is often used to convert private address domains and public address domains to solve the problem of lack of IP addresses. After NAT is implemented on the firewall, the internal topology of the protected network can be hidden, and the security of the network can be improved to a certain extent. If reverse NAT provides dynamic network address and port translation functions, it can also implement functions such as load balancing. Bastion host: A hardened computer capable of defending against attacks, exposed on the Internet, as a checkpoint to enter the internal network, so as to concentrate the security problems of the entire network on a certain host, thus saving time and effort , Regardless of the security purpose of other hosts. 2. Common hardware firewalls on the market (1) NetScreen 208 Firewall The NetScreen firewall product launched by NetScreen Technology is a new type of network security hardware product. NetScreen uses built-in ASIC technology, and its security devices have low-latency, efficient IPSec encryption and firewall functions, and can be seamlessly deployed to any network. The installation and operation of the device are also very easy, and can be managed through a variety of management interfaces including the built-in WebUI interface, command line interface or NetScreen central management solution. NetScreen integrates all functions into a single hardware product. It is not only easy to install and manage, but also provides higher reliability and security. Because NetScreen devices do not have the stability problems of other brands of products on hard drives, it is the best solution for users with extremely high online time requirements. With NetScreen devices, you only need to configure and manage firewall, VPN, and traffic management functions, eliminating the need to configure additional hardware and complex operating systems. This approach shortens the time for installation and management, and omits the steps of setting up to prevent security vulnerabilities. NetScreen-100 Firewall is more suitable for the network security needs of medium-sized enterprises. (2) Cisco Secure PIX 515-E Firewall The Cisco Secure PIX firewall is a dedicated firewall facility in the Cisco firewall family. The Cisco Secure PIX 515-E firewall system provides a high degree of security through an organic combination of end-to-end security services. It is suitable for remote sites that only need two-way communication with their own corporate network, or when the corporate network provides all Web services on their corporate firewall. The Cisco Secure PIX 515-E is different from the ordinary CPU-intensive dedicated proxy server (a large amount of processing is required for each packet at the application level). The Cisco Secure PIX 515-E firewall uses a non-UNIX, secure, real-time built-in system. It can provide the characteristics of expanding and reconfiguring the IP network without causing the problem of IP address shortage. NAT can use the existing IP address or the address specified by the Internet designated number agency [IANA] reserved pool [RFC.1918] to achieve this feature. Cisco Secure PIX 515-E can also selectively allow addresses to be converted as needed. CISCO guarantees that NAT will work with all other PIX firewall features (such as multimedia application support). Cisco Secure PIX 515-E Firewall is more suitable for the network security needs of small and medium-sized enterprises. (3) Tianrongxin Network Guardian NGFW4000-S firewall The network guard of Beijing Tianrongxin Company is the first firewall system with independent copyright in China, which is widely used in telecommunications, electronics, education, scientific research and other units in China. It consists of firewall and manager. Network Guardian NGFW4000-S firewall is China's first nuclear detection firewall, more secure and stable. Network Guardian NGFW4000-S firewall system integrates packet filtering firewall, application proxy, network address translation (NAT), user identity authentication, virtual private network, Web page protection, user permission control, security audit, attack detection, flow control and billing And other functions can provide a full range of network security services for different types of Internet access networks. The network guard firewall system is designed by the Chinese themselves, so the management interface is completely Chinese culture, which makes the management more convenient. The management interface of the network guard NGFW4000-S firewall is the most intuitive of all firewalls. Network Guardian NGFW4000-S firewall is more suitable for the network security needs of medium-sized enterprises. (4) Neusoft NetEye 4032 firewall The NetEye 4032 firewall is the latest version of the NetEye firewall series. The system has greatly improved in performance, reliability, and management. Its flow filtering architecture based on stateful packet filtering ensures complete high-performance filtering from the data link layer to the application layer. It can upgrade application-level plug-ins in a timely manner, respond to attacks in a timely manner, and dynamically guarantee network security. NetEye Firewall 4032 optimizes the flow filtering engine, further improving performance and stability, while enriching application-level plug-ins, security defense plug-ins, and increasing the speed of developing corresponding plug-ins. Network security itself is dynamic, its changes are very rapid, and new attacks may occur every day. The security strategy must be able to be dynamically adjusted with the generation of attacks, so that the security of the network can be protected dynamically. The flow filtering architecture based on stateful packet filtering has the characteristics of dynamically protecting network security, enabling NetEye firewall to effectively resist various new attacks and dynamically guarantee network security. Neusoft NetEye 4032 firewall is more suitable for the network security needs of small and medium-sized enterprises. Third, the basic configuration of the firewall Let me take the domestic firewall first brand Tianrongxin NGFW 4000 as an example to explain to you how to configure the firewall in a typical network environment. NGFW4000 has 3 standard ports, one of which is connected to the external network (Internet network), one is connected to the internal network, and the other is connected to the DMZ zone. There is a network server in the DMZ zone. The effect to be achieved by installing the firewall is: computers in the internal network zone can access the external network arbitrarily, and can access the network server specified in the DMZ. Internet and DMZ computers cannot access the internal network; Internet network can access the server in the DMZ. 1. Configure the management port Tianrongxin Network Guardian NGFW4000 firewall is composed of a firewall and a manager. The management of the firewall is implemented by a computer in the network. By default, none of the three ports are management ports, so we first need to connect the Tianrongxin Network Guardian NGFW4000 firewall to our computer through the serial port, assign a management port to the firewall, and later set the firewall to remote Came true. Use a serial cable to connect the serial port (COM1) of the computer to the console port of the NGFW4000 firewall, start the computer's "super terminal", select COM1 for the port, set the communication parameters to 9600 bits per second, 8 data bits, and no parity , Stop bit 1, no data flow control. Enter the HyperTerminal interface, enter the firewall password to enter the command line format. Define the management port: if eth1 XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX 255.255.255.0 Modify the GUI login authority of the management port: fire client add topsec -t gui -a extranet-i 0.0.0.0-255.255.255.255 2. Use the GUI management software to configure the firewall Install Tianrongxin firewall GUI management software "TOPSEC centralized manager", and establish NGFW4000 management project, enter the IP address and description of firewall management port. Then log in to enter the management interface. (1) Define the network area Internet (external network): connected to eth0, the default access policy is any (that is, the default is readable and writable), the log option is empty, and ping, GUI, and telnet are prohibited. Intranet: Connected to eth1, the default access policy is none (unreadable and unwritable), and the log option is to record user commands, allowing ping, GUI, and telnet. DMZ zone: connected to eth2, the default access policy is none (unreadable and unwritable), the log option is to record user commands, and ping, GUI, and telnet are prohibited. (2) Define network objects A network node represents a physical machine in a certain area. It can be used as the source and destination in the access strategy, and also as the source and destination in the communication strategy. The network node can also be used as an address pool for address mapping, which represents the actual machine for address mapping. See the communication strategy for a detailed description. Subnet represents a continuous IP address. It can be used as the source or destination of a policy, and can also be used as a NAT address pool. If there are IPs in the subnet segment that have been used by other departments, in order to avoid using three subnets to describe the IP addresses used by the technical department, you can specify the two addresses occupied by other departments in the exception addresses. In order to configure the access policy, first define special nodes and subnets: FTP_SERVER: stands for FTP server, zone = DMZ, IP address = XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX. HTTP_SERVER: stands for HTTP server, zone = DMZ, IP address = XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX. MAIL_SERVER: stands for mail server, zone = DMZ, IP address = XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX. V_SERVER: Represents the virtual server accessed by the external network, area = Internet, IP = firewall IP address. inside: All machines on the intranet, area = Intranet, start address = 0.0.0.0, end address = 255.255.255.255. outside: All machines on the external network, area = Internet, start address = 0.0.0.0, end address = 255.255.255.255. (3) Configure access strategy Add three access strategies in the DMZ area: A. Access destination = FTP_SERVER, destination port = TCP 21. Source = inside, access rights = read, write. Source = outside, access rights = read. This configuration means that users on the internal network can read and write files on the FTP server, while users on the external network can only read files and cannot write files. B. Access purpose = HTTP_SERVER, destination port = TCP 80. Source = inside + outside, access rights = read and write. This configuration means that users on the internal and external networks can access the HTTP server. C. Access purpose = MAIL_SERVER, destination port = TCP 25, TCP 110. Source = inside + outside, access rights = read and write. This configuration means that users on the internal and external networks can access the MAIL server. (4) Communication strategy Since machines on the internal network do not have legal IP addresses, they need to perform address translation when accessing the external network. When an internal machine accesses an external machine, its address can be converted into a firewall address or an address in an address pool. Add a communication strategy, destination = outside, source = inside, mode = NAT, destination port = all ports. If you need to convert to an address in an address pool, you must first define a subnet in the Internet, the address range is the range of the address pool, then select the NAT method in the communication strategy, select the address just defined in the address pool type Pool. The server also does not have a legal IP address, and must rely on the firewall to do address mapping to provide external services. Increase communication strategy. A. Destination = V_SERVER, source = outside, communication method = MAP, specified protocol = TCP, port mapping 21-> 21, target machine = FTP_SERVER. B. Destination = V_SERVER, source = outside, communication method = MAP, specified protocol = TCP, port mapping 80-> 80, target machine = HTTP_SERVER. C. Destination = V_SERVER, source = outside, communication method = MAP, specified protocol = TCP, port mapping 25-> 25, target machine = MAIL_SERVER. D. Destination = V_SERVER, source = outside, communication method = MAP, specified protocol = TCP, port mapping 110-> 110, target machine = MAIL_SERVER. (5) Special port There is no special port we need to use in the default port definition of the firewall, so we need to manually add these special ports. Select "Advanced Management"> "Special Objects"> "Special Ports" in the firewall centralized manager, a special port definition interface will pop up, click "Define New Object", enter the special port number and definition area. (6) Other configuration Finally, enter the "Tools" option to define the firewall administrator, permissions, and linkage with IDS. (Figure 8) Four, firewall comparison After understanding the working principle and basic configuration of the firewall, let me introduce you to NetScreen 208, Cisco PIX 515E, NGFW 4000-S, NetEye 4032, the four most common hardware firewalls in the market in terms of basic performance, operation management and market price. Comparison. Firewall NetScreen208 CiscoPIX515E NGFW4000-S NetEye4032 Core Technology State detection State detection Nuclear testing State detection product type ASIC hardware hardware equipment hardware equipment hardware equipment Working mode (routing mode, bridge mode, mixed mode) Routing mode, bridge mode Routing mode, bridge mode Routing mode, bridge mode, Mixed mode Routing mode, bridge mode Number of concurrent connections 130000 130000 600000 300000 Network throughput 550M 170M 100M 200M Maximum support network interface 8 6 12 8 operating system ScreenOS Dedicated operating system Dedicated operating system Dedicated operating system Management method Serial port, CLI, Telnet, Web, GUI Serial port, Telnet, Web, GUI Serial port, Telnet, Web, GUI Serial port, Telnet, GUI Market quotation 142,000RMB 80,000RMB 138,000RMB 148,000RMB Asymmetric Thyristor is the abbreviation of thyristor, also known as silicon controlled rectifier, formerly referred to as thyristor; thyristor is PNPN four-layer semiconductor structure, it has three poles: anode, cathode and control pole; thyristor has silicon rectifier The characteristics of the parts can work under high voltage and high current conditions, and their working processes can be controlled and widely used in electronic circuits such as controlled rectifiers, AC voltage regulators, contactless electronic switches, inverters, and inverters. Asymmetric Thyristor,60Ma Asymmetric Thyristor,Oem Asymmetric Thyristors,Electronic Component Asymmetric Thyristor YANGZHOU POSITIONING TECH CO., LTD. , https://www.cnchipmicro.com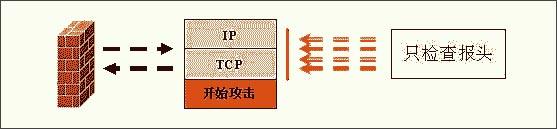
Figure 1: Working principle diagram of packet filtering firewall 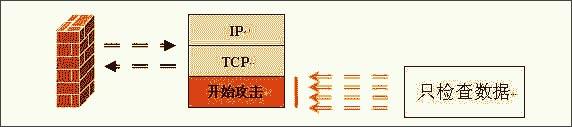
Figure 2: Working principle diagram of application gateway firewall 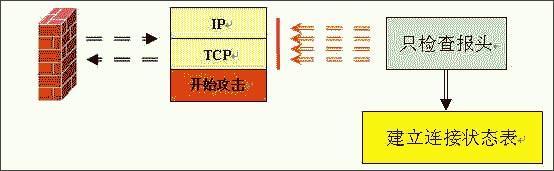
Figure 3: Working principle diagram of the status detection firewall 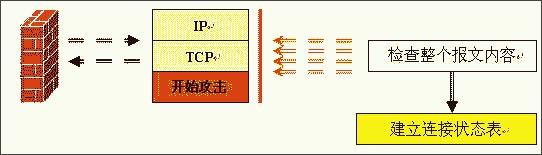
Figure 4: Working principle diagram of composite firewall 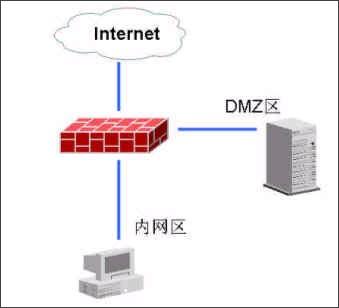
Figure 5: Network topology 
Image 6 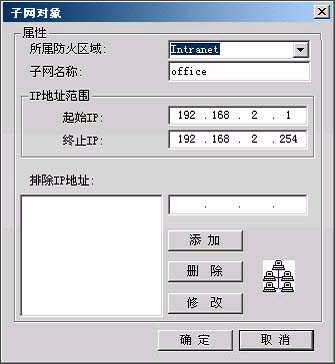
Picture 7 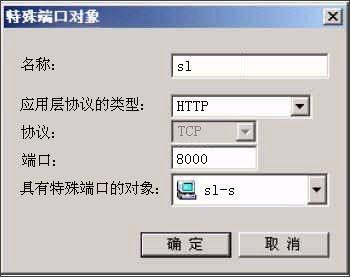
Picture 8