When the PN junction is applied with a forward voltage, it can have a large forward diffusion current, that is, it exhibits low resistance. We call the PN junction conduction; when the PN junction is applied with a reverse voltage, there is only a small reverse drift current, showing high resistance , We call PN junction cut-off. This is the unidirectional conductivity of the PN junction. The PN junction has unidirectional conductivity. If the applied voltage causes the current to flow from the P area to the N area, the PN junction has low resistance, so the current is large; on the contrary, it is high resistance and the current is small. If an external voltage is applied: the potential of the P area of ​​the PN junction is higher than the potential of the N area is called forward voltage, referred to as forward bias; the potential of the PN junction P area is lower than the potential of the N area is called reverse voltage, referred to as reverse bias . (1) Conduction situation when PN junction is applied with forward voltage Part of the applied forward voltage falls on the PN junction area, and the direction is opposite to the direction of the electric field in the PN junction, which weakens the internal electric field. As a result, the resistance of the internal electric field to the diffusion movement of the multitons is weakened, and the diffusion current is increased. The diffusion current is much larger than the drift current, and the influence of the drift current can be ignored, and the PN junction exhibits low resistance. (2) Conduction situation when PN junction is applied with reverse voltage Part of the applied reverse voltage falls on the PN junction area, and the direction is the same as the direction of the electric field in the PN junction, which strengthens the internal electric field. The resistance of the internal electric field to the multiton diffusion movement is enhanced, and the diffusion current is greatly reduced. At this time, the drift current formed by the minority carriers in the PN junction region under the action of the internal electric field is greater than the diffusion current, and the diffusion current can be ignored, and the PN junction exhibits high resistance. Under certain temperature conditions, the minority carrier concentration determined by the intrinsic excitation is constant, so the drift current formed by the minority carrier is constant and basically has nothing to do with the magnitude of the applied reverse voltage. This current is also called the reverse saturation current. When a forward voltage is applied to the PN junction, it exhibits low resistance and a large forward diffusion current; when a reverse voltage is applied to the PN junction, it exhibits a high resistance and has a small reverse drift current. It can be concluded that: PN junction has unidirectional conductivity. 1. The forward bias of the PN junction 2. Reverse bias of PN junction 1. When the PN junction is forward biased, the PN junction becomes narrower; the multi-carrier diffusion movement is strengthened, and the minority carrier drifting movement is weakened; the PN junction is in a conducting state. 2. When the PN junction is reversely biased, the PN junction becomes wider; the multi-carrier diffusion motion is weakened, and the minority carrier drifting motion is strengthened; the PN is in a cut-off state. 3. When the PN junction is reverse biased, the reverse saturation current is Is Adapter Ring,Lens Adapter Ring,Camera Adapter Ring,Filter Adapter Ring SHAOXING COLORBEE PLASTIC CO.,LTD , https://www.fantaicolorbee.com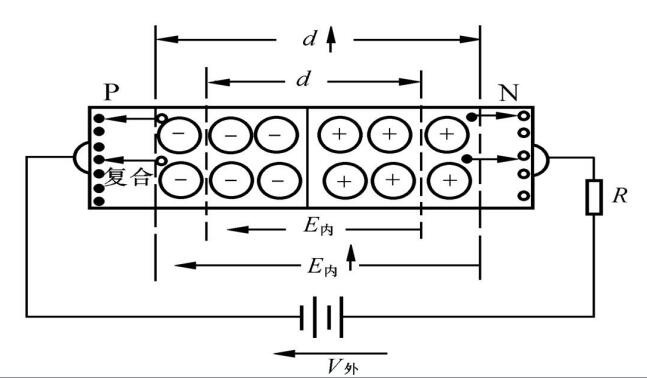
pn junction unidirectional conductivity
var videoObject = {container:'.video', variable:'player', autoplay: true, html5m3u8: true, video: "https://vdse.bdstatic.com//a5399f6563ebb6b3403ee208ce287221?authorization=bce-auth-v1%2F40f207e648424f47b2e3df1014b1a5 %2F2017-05-11T09%3A02%3A31Z%2F-1%2F%2Fc030d9f573d123f795238decb71a7d5e4c3ccd88932462e3387861a30f3ea129" }; if (!! window.ActiveXObject) {videoObject.html5m3u8 = false} varvideo player Object; unidirectional conductivity