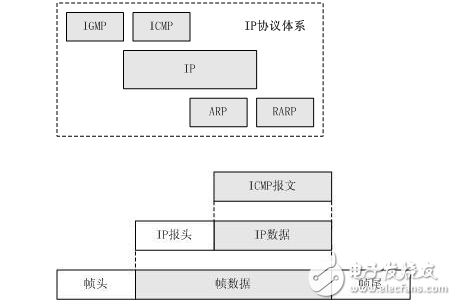
ICMP is the Internet Control Message Protocol (Internet Control Message Protocol) protocol. It is a sub-protocol of the TCP/IP protocol suite for passing control messages between IP hosts and routers. The control message refers to the network itself, such as the network is unreachable, the host is reachable, and the route is available. Although these control messages do not transmit user data, they play an important role in the transmission of user data. The ICMP protocol is a connectionless protocol for transmitting error reporting control information. It is a very important protocol and it is extremely important for network security. It is a sub-protocol of the TCP/IP protocol family and belongs to the network layer protocol. It is mainly used to transfer control information between the host and the router, including reporting errors, exchange limited control, and status information. ICMP messages are automatically sent when IP data cannot be accessed and the IP router cannot forward packets at the current transmission rate. The value of the ICMP packet in the header protocol type field (Protocol 8bit) of the IP frame structure is 1. As shown in the following figure, the ICMP packet has an 8-byte long header, where the first 4 bytes are in a fixed format, including an 8-bit type field, an 8-bit code field, and a 16-bit checksum; the last 4 bytes. Different values ​​are taken depending on the type of ICMP packet. ICMP provides consistent and error-prone information. The sent error message is returned to the device that sent the original data, because only the sending device is the logical recipient of the error message. The sending device can then determine the type of error that occurred based on the ICMP message and determine how to better retransmit the failed packet. But the only function of ICMP is to report the problem instead of correcting the error, and the task of correcting the error is done by the sender. We often use the ICMP protocol in the network. For example, we often use the Ping command to check the network (both in Linux and Windows). This "Ping" process is actually the process of working with the ICMP protocol. There are other network commands such as tracert Tracert commands that are also based on the ICMP protocol. The icmp protocol is a subsidiary protocol of the IP layer and is a protocol between the IP layer and the TCP layer. It is generally considered to belong to the IP layer protocol. The IP protocol uses it to exchange error messages and other network conditions with other hosts or routers. The ICMP packet carries the control information and the failure recovery information. It is mainly used to control the error that the router host sends error packets to other routers or hosts. ICMP itself is a protocol at the network layer; The ICMP error report uses the router-source host mode. When the router finds an error in the datagram transmission, the router only reports the cause of the error to the source host. ICMP does not guarantee that all IP datagrams can be transmitted to the destination host; ICMP can't correct the error, it just reports the error. Error handling needs to be done by high-level protocols. It is a sub-protocol of the TCP/IP protocol suite for passing control messages between IP hosts and routers. The control message refers to the network itself, such as the network is unreachable, the host is reachable, and the route is available. Although these control messages do not transmit user data, they play an important role in the transmission of user data. The role and characteristics of ICMP ICMP features: ICMP itself is a protocol at the network layer; ICMP error reporting uses the router-source host mode, the router only reports the cause of the error to the source host when it finds an error in the datagram transmission; ICMP does not guarantee All IP datagrams can be transmitted to the destination host; ICMP cannot correct the error, it just reports the error. Error handling needs to be done by high-level protocols. ICMP message type ICMP error control ICMP error report message: Destination station unreachable: Source station suppression timeout parameter problem Change route destination station Unreachable network unreachable (host unreachable) Host unreachable Protocol unreachable (protocol unreachable) ) port unreachable source route failed (source route failed) destination network agnostic (unknown desTInaTIon network) destination host agnostic (unknown desTInaTIon host) The present invention provides a method for controlling the temperature of a flue-cured electronic cigarette and a flue-cured electronic cigarette. The flue-cured electronic cigarette includes an N-section heating body, where N is an integer greater than 1, and the heating body is used for heating tobacco. The method for controlling the temperature of the flue-cured electronic cigarette includes: the flue-cured electronic cigarette heats the i-th heating body, and i is an integer greater than 0 and less than N; after the first preset time, the flue-cured electronic cigarette pairs the i+ The first stage heating body is heated; after the second preset time, the flue-cured electronic cigarette stops heating the i-th stage heating body, and continues to heat the i+1th stage heating body. The technical solution solves the problem of unbalanced smoke output of flue-cured electronic cigarettes during multi-stage heating.The present invention provides a method for controlling the temperature of a flue-cured electronic cigarette and a flue-cured electronic cigarette. The flue-cured electronic cigarette includes an N-section heating body, where N is an integer greater than 1, and the heating body is used for heating tobacco. The method for controlling the temperature of the flue-cured electronic cigarette includes: the flue-cured electronic cigarette heats the i-th heating body, and i is an integer greater than 0 and less than N; after the first preset time, the flue-cured electronic cigarette pairs the i+ The first stage heating body is heated; after the second preset time, the flue-cured electronic cigarette stops heating the i-th stage heating body, and continues to heat the i+1th stage heating body. The technical solution solves the problem of unbalanced smoke output of flue-cured electronic cigarettes during multi-stage heating. E-Cigarette Starter Kits,small e cigarette starter kit,mini e cigarette starter kit,e cig starter kit near me,cheapest e cigarette starter kit, e cigarette starter kits,electronic cigarette starter kits Suizhou simi intelligent technology development co., LTD , https://www.msmvape.com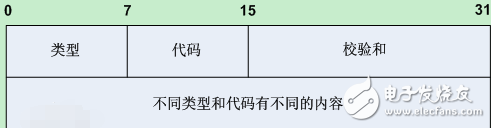
Which layer does the icmp protocol belong to? What are the characteristics?
What is the icmp protocol