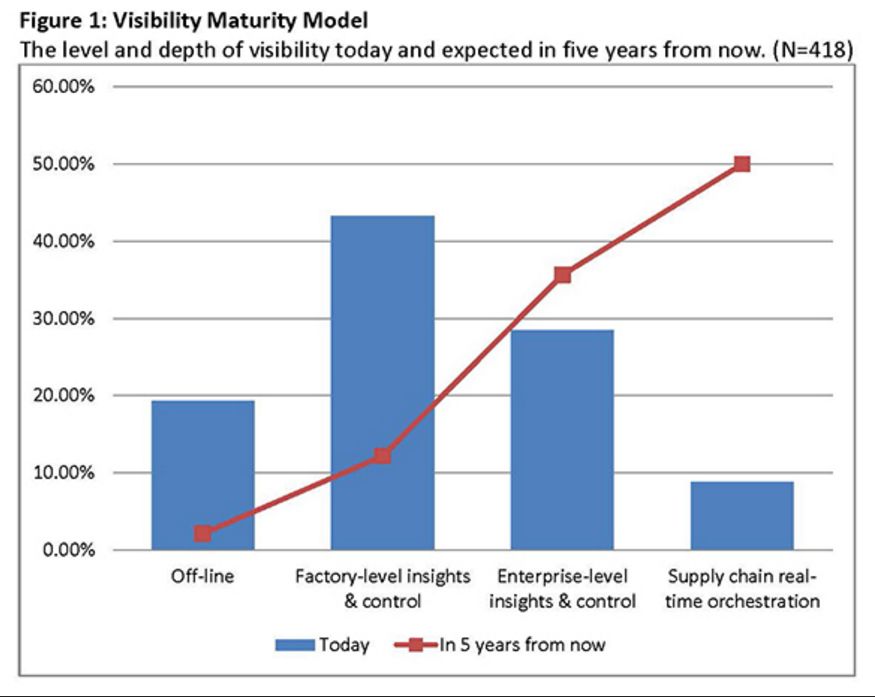
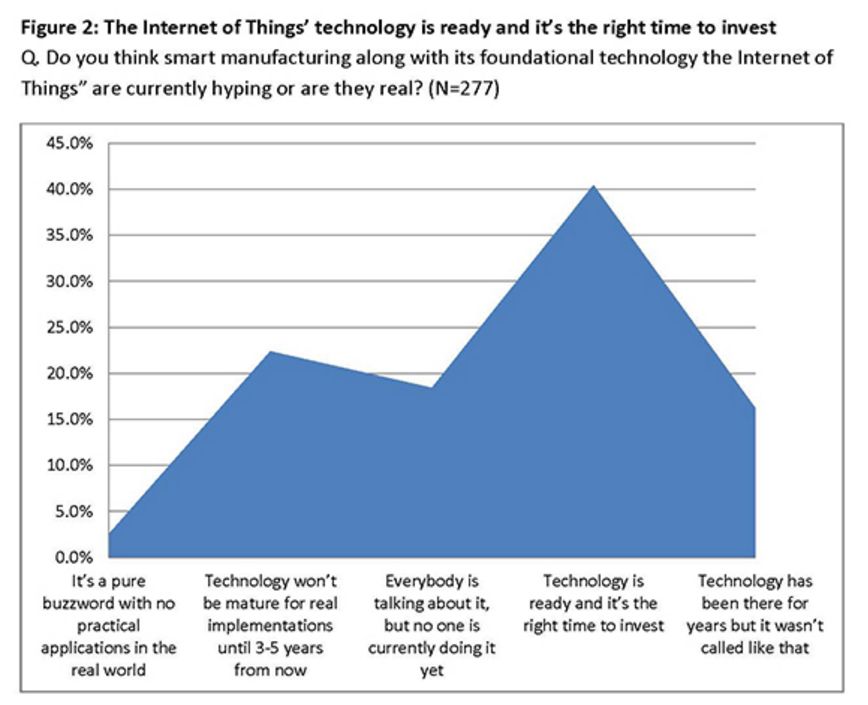
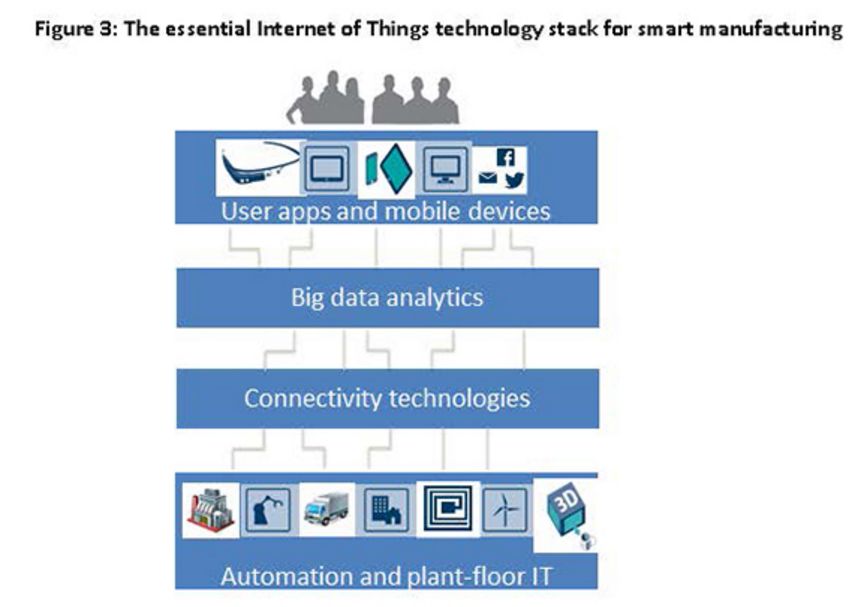
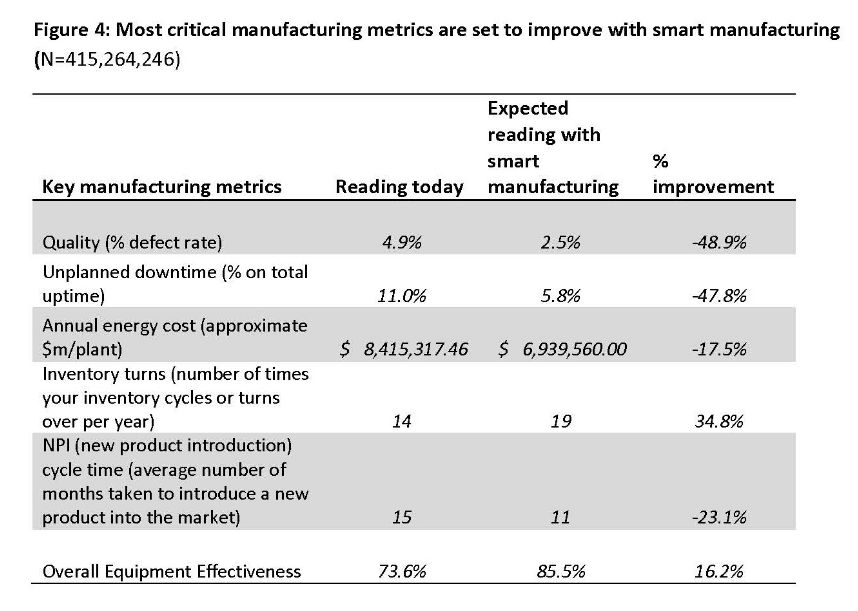
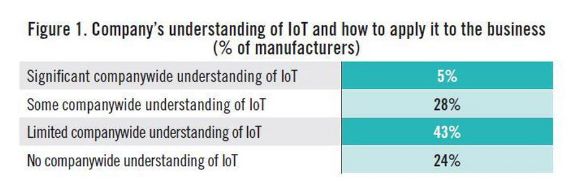
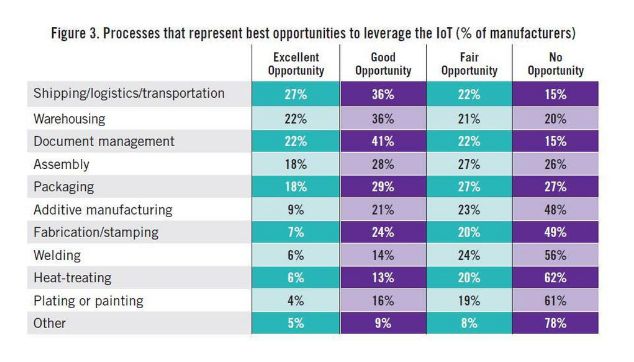
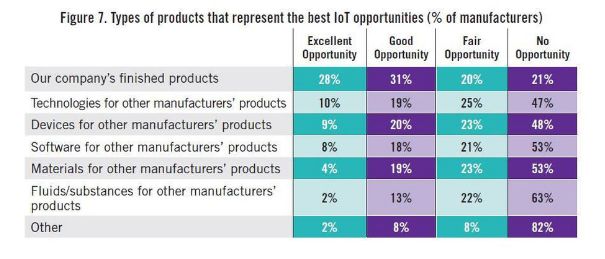
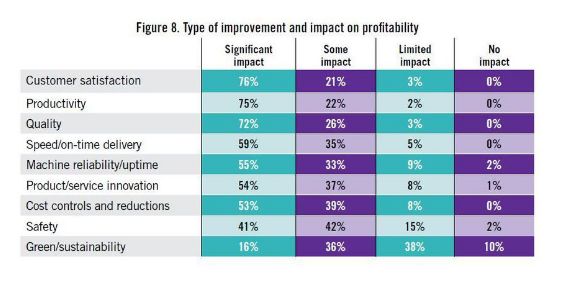
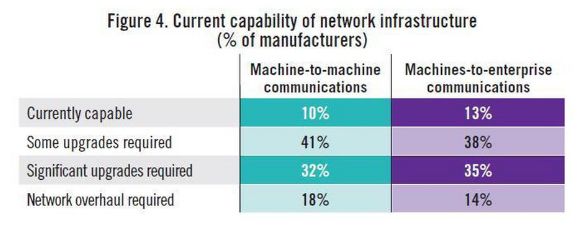
High-level officials in the central government advocated "Made in China 2025" on different occasions. Premier Li has repeatedly mentioned that from a manufacturing power to a manufacturing power, a very important part of a manufacturing power is "Made in China", of which the Internet of Things and Industry 4.0 are critical. Application, then how does the Internet of Things change the manufacturing industry? How does the Internet of Things make us smarter? How are foreign industrial manufacturing and innovation giants playing the Internet of Things? How do European and American developed countries view the Internet of Things, and what is their overall development status? Today, Lao Zeng will bring his classmates to chat, and welcome friends who are interested to communicate. The Internet of Things (IoT) is changing our manufacturing A factory connected to the Internet is more efficient, smarter and more cost-effective than a factory without a connection. In a market, companies increasingly need to maximize their potential to survive and develop, while those without connectivity are falling behind. According to Rockwell Automation's (Rockwell) vice president of market development, John Nesi, only 10% of industrial operations are currently using the Internet of Things. The company connects businesses to cyberspace to improve manufacturing capabilities. He said: "Global competitive pressures are challenging industrial and manufacturing companies, and inefficient companies will gradually be eliminated." Improved experience efficiency of IoT enterprises Nesi said King's Hawaiian, one of Rockwell's food and beverage customers, was able to add an additional 180,000 pounds of bread a day, doubling its previous output after installing the new technology. King's Hawaiia installed 11 connected machines in a new factory. These machines are connected to FactoryTalk. The software allows the company's employees to remotely access historical and real-time data, and can also use the production dashboard to fully understand the entire system for monitoring performance. All these software and hardware have brought "faster time to market (faster time to market), better asset utilization and optimization, lower total cost of ownership), higher labor efficiency, and enterprise Risk management and smarter expenditures,†Nesi said. The new system reduces maintenance costs and downtime, and adds more data capabilities. In turn, Nesi said: "This allows them to aggregate data and present it on an accessible dashboard, allowing managers to monitor operations and KPIs across the enterprise." Since King's Hawaiian's and other systems are connected to the Internet, they can be controlled and managed through a remote operation center. This allows global companies to build factories around the world and monitor them in real time. Another company that has gained the advantage of connected systems (IOT, Internet of Things) is General Electric. At the Durathon battery factory in Schenectady, New York, the Internet of Things helps the company collect process data around the clock. With 10,000 sensors on the assembly line and sensors in each battery, managers can instantly understand the production status. They can share this information and data with colleagues in other departments. According to David Stephenson of O'Reilly, the technologies of General Electric and similar manufacturers have created unprecedented innovations. "The Internet of Things is expected to eliminate a large amount of information gaps about real-time conditions on the factory floor, fully optimize production and eliminate waste," he said. Reduce safety hazards in the workplace Sine-Wave, which focuses on enterprise technology solutions, has created a customized IoT plan to improve the safety and communication capabilities of the mine. According to their website, they designed a browser-based application that allows users to communicate with workers, operators, and machines in the mine, as well as "see a real-time view of all activities underground, including mining operations." By real-time understanding of what is happening in the underground mine, users can avoid safety hazards and quickly respond to emergencies. Cybersecurity risk Michael Assante of the SANS Institute said that when manufacturers use IoT in their factories, they should weigh the risks. Before connecting, the security team should be confident "understand the exposed protocols, interfaces/configurations, system software, firmware and authentication controls." Over time, these safety precautions will become more and more important. "The number of connected terminals is expected to be close to 50 billion in the next five years," Nesi said. "Over time, every terminal in the manufacturing industry-be it sensors, valves, instruments, or machines-will provide intelligence for larger information systems." The Internet of Things will make manufacturing more intelligent The global manufacturing industry is on the cusp of a revolution. As we saw in the early versions of factory and enterprise software, new information technology suddenly not only provided jobs that make manufacturing management more effective, but the jobs themselves were smarter. Technology based on the Internet of Things may fundamentally improve the visibility of manufacturing, so that every step of the production process can "see" every production unit. Batch-level visibility is being replaced by unit-level visibility. This is the dawn of smart manufacturing. The transformation is huge. A recent field survey conducted by SCM World on smart manufacturing and the Internet of Things found that although today one in five people admit that their factory operations are completely "off the Internet," this number will drop to close to zero in five years. In fact, according to SCM World's visibility maturity model (Figure 1), half of all manufacturing executives surveyed want visibility in the supply chain at the unit level. Only 10% predict that they are still limited to a single factory-level understanding and control. Smart manufacturing is about creating an environment where all available information from factories and supply chains is captured in real time, becomes visible and transformed into actionable. Smart manufacturing encompasses all aspects of the business, blurring the boundaries between factory operations, supply chain, product design, and demand management. Intelligent manufacturing can virtually track assets, processes, resources, and products to provide enterprises with sufficient visibility to support streamlining business processes and optimize supply and demand. In essence, smart manufacturing is a decision-making environment. It is very important that smart manufacturing includes active and autonomous analysis functions, making smart manufacturing an intelligent and self-healing environment. Smart manufacturing companies can predictably meet business needs through smart and automated actions that are driven by previously unavailable physical worlds. Intelligent manufacturing transforms enterprises into proactive and autonomous organizations that can predict and repair potential destructive problems, develop operations and bring joy to customers, while increasing profitability. Many leading global manufacturers, including Bosch, Cisco, FCA (Fiat Chrysler Automobiles), GE, General Mills, Harley-Davidson and Siemens, are early adopters of smart manufacturing (or Industry 4.0) in their factories. Interesting examples include: Siemens. At the Siemens electronics manufacturing plant in Amberg, Germany, machines and computers autonomously handle 75% of the value chain. From one end of the production line to the other, about 1,000 automation controllers are running. The parts being produced communicate with the machine through the product code. The product code tells the machine their production requirements and the next steps to be taken. All processes are optimized for IT control to achieve the lowest failure rate. Employees are mainly responsible for overseeing production and technical assets, including handling emergencies. General Electric GE. At GE's Durathon battery factory, more than 10,000 sensors measure temperature, humidity, air pressure and machine operating data in real time. This not only provides the opportunity to monitor the production and adjustment process in real time, but also to trace battery performance, back to a specific batch of powder and every step in the process. Harley-Davidson. Harley-Davidson's main production facility in York, Pennsylvania, and every asset in the production workshop are connected, and every step in production is tracked and incorporated into the real-time performance management system. Cisco. In order to better coordinate its global network of outsourced production plants, Cisco has developed a "virtual" manufacturing execution system platform (VMES) that provides real-time visibility of production operations. The system uses technologies such as cloud, big data analysis and the Internet of Things to connect and collect real-time information from production machines, thereby achieving predictive quality functions in a fully outsourced manufacturing environment. Intelligent manufacturing needs to use healthy technology to ensure that machines work together, display material flows in real time, and engineer teams to coordinate the entire process. The Internet of Things is the technological environment that makes this possible. In factory floor applications, the Internet of Things can create a network, from production equipment to production parts, from sensor embedded automation control to energy meters, from trucks to smart shelves in warehouses, to connect various manufacturing assets. Through the Internet of Things, manufacturers can provide a digital identity for each physical asset, enabling them to understand the exact location and condition of these assets in real time throughout the supply chain. The right time to invest Manufacturers all over the world are now confident. About 40% of respondents believe that smart manufacturing and its basic technology-the Internet of Things are ready, and now is the right time to invest (Figure 2). Only 3% of people regard smart manufacturing and the Internet of Things as pure buzzwords. For those who are ready, smart manufacturing is essentially a platform that integrates multiple technologies, such as connectivity technology (a network that enables objects to connect to the Internet), cloud (a computing and storage environment where assets can communicate), and big data Analysis (system intelligence that can analyze data and provide insight). The idea is to use connection technologies (for example, industrial networks, wifi, M2M, etc.) to integrate factory automation assets (for example, production equipment, robots, RFID, etc.) with end-user applications (for example, MES, PLM, ERP, etc.) and mobile devices. Active and accurate business decisions. Figure 3 shows the basic technology of the Internet of Things for our smart manufacturing applications. In our field survey, we also asked about the expected performance results of the smart manufacturing industry, and found high expectations. Benefits in terms of quality, uptime, inventory efficiency, etc. are expected to reach double-digit percentages (Figure 4). The Internet of Things has an eye-catching halo, but the imagination is almost too far-reaching for many possibilities. When this concept is applied to specific applications, especially when combined with other transformative technologies, its potential becomes clear. For manufacturers, the possible impact of IoT in the field of smart manufacturing is indeed very large. Internet of Things (IoT) research data in manufacturing In the next two years, 76% of manufacturers will increase the use of smart devices or embedded intelligence in the manufacturing process. 63% of manufacturers have or are planning to integrate IoT technology into their products. 58% of manufacturers said that improving product quality is the most important goal they pursue by integrating smart devices or embedding intelligence. 44% of manufacturers stated that their biggest obstacle to using IoT is their company's limited knowledge of how IoT can improve operations and products. These and many other insights come from MPI Group’s IoT research. The research is based on interviews with Rockwell Automation, QAD and 350 manufacturers in August and September 2015, and BDO also sponsored the research. Despite the high interest of almost every company, only 10% of manufacturers today have implemented IoT strategies. The main contents of this research include: 71% of manufacturers said that the Internet of Things will have a significant impact (24%) or some impact (47%) on their business in the next five years, but there are still 24% of companies that do not fully understand the Internet of Things. Although most manufacturers recognize the value of the Internet of Things, there is a significant knowledge gap in how to best plan and utilize these technologies. 76% of manufacturers will add the use of smart devices or embedded intelligence to the manufacturing process within the next two years. 66% will increase non-production IoT applications. Manufacturers believe that transportation, warehousing and document management are the best opportunities to improve operational accuracy and performance. The following table provides a process analysis that represents the best opportunity to take full advantage of IoT. According to the manufacturer, existing products (28%) using IoT technology are the best opportunity. Providing IoT technology for other manufacturers' products (10%) and other manufacturers' equipment (9%) are the three most attractive opportunities for manufacturers. The table below compares the opportunity rankings of product categories based on survey data. Increasing customer satisfaction (76%), increasing productivity (75%) and improving product quality (72%) are the biggest improvements manufacturers expect to affect profitability. Other areas where the IoT strategy is expected to make a substantial contribution include speed and on-time delivery (59%), machine reliability and uptime (59%), and product and service innovation (54%). The study also found that manufacturers are focusing on improving cost control and reduction (53%), safety (41%) and achieving sustainable development goals (16%). Currently only 10% of manufacturers have a network capable of machine-to-machine communication. 41% expect some upgrades to their networks, and 32% said they need major upgrades to achieve machine-to-machine integration. 18%, or close to one-fifth, their systems will need to be overhauled. The following table compares the manufacturer's machine-to-machine and machine-to-business communication capabilities. Most manufacturers plan to embed smart devices in their products. New products and increased revenue in market share (both 39%) are the most revolutionary goals. Other goals include obtaining data on products or services in the field (34%), increasing the profit margin of each product (34%), increasing brand and market awareness (27%), and entering new markets/sectors (26%). 58% of manufacturers said that improving product quality is the most important goal they pursue by integrating smart devices or embedding intelligence. By adopting IoT technology, the top five goals pursued by manufacturers are to improve operational performance and speed (57%), reduce manufacturing costs (57%), improve manufacturing equipment maintenance and uptime (47%), and improve business analysis information (42%). Recognizing and understanding the opportunities/benefits of the Internet of Things (44%) and scalable to handle the network functions of the Internet of Things (38%) are two major challenges facing manufacturers today. Other challenges include developing or expanding the budget and resources of IoT plans (37%), including smart devices or embedded intelligence (37%, adapting to existing technologies (36%). China Industrial Internet of Things In 2016, the output value of China's industrial Internet of Things was 189.6 billion yuan, about 18% of the overall Internet of Things industry. It is estimated that by 2020, the industrial Internet of Things will account for 25% of the overall Internet of Things industry, exceeding 450 billion yuan. The Industrial Internet of Things is the application of the Internet of Things in the industrial field. It will have important applications in energy, logistics (including railways and stations, airports, ports), manufacturing (mining, oil and gas, supply chain, machinery manufacturing) and other fields. The author was fortunate to interview Roger Da, a global Internet of Things expert. Mr. Roger once served the world’s top Internet of Things application companies Zebra Technology Co., Ltd. and Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., and once helped Boeing in the United States and Bombardier in Canada lead IoT solutions For deployment, he also served as the chief architect and helped the Kunshan municipal government build a smart city. Regarding domestic IoT applications, he mentioned: The main problem of China’s industrial IoT is the lack of compound talents, familiar with the overall architecture and solutions, and at the same time There are few talents who are familiar with the platform, software and firmware. In addition, China’s infrastructure is relatively weak. Many private manufacturing industries still operate in large-scale workshops. The deployment of relatively complete Internet of Things and Industry 4.0 are in very basic conditions. In addition, in the development and deployment of the entire program, capital investment may also be a relatively obvious problem. He said that the entire market needs more experts to train. It is very important for companies and governments to share some technologies, applications and actual results and some overseas advanced and mature cases, as well as relevant knowledge and professional teaching. In addition, the government, industry organizations dominate more summit forums, and self-media communication is of great significance to the expansion of the market. The government establishes special funds, establishes pilot projects and helps enterprises to establish templates (DEMOs, which are positive for the entire industry. The old Zeng Wechat1638881963 hopes to become an industry thought promoter and advocate, and also hopes that experienced old masters and drivers will join in and work together to promote the development of the industry, truly promote China’s smart manufacturing, and promote China’s manufacturing 2025. Others Lithium Ion Battery,Lithium Battery 6 Volt,Lithium Ion 9V Battery,Lithium Ion 6V Battery Langrui Energy (Shenzhen) Co.,Ltd , https://www.langruibattery.com