Full HD TVs have begun to win the favor of consumers. At present, LCD TVs of 24 or more inches are able to support full HD, and from a practical point of view, only full HD TVs of 37 inches or more can bring better display and viewing experience to consumers. Therefore, larger LCD TVs will lead the future full HD market. This article refers to the address: http:// However, the pursuit of better visual effects has also brought much greater power challenges than ever before. Higher power consumption will not only increase the electricity bills of consumers, but also will not cooperate with the macro promotion of energy saving and consumption reduction in various countries. Various governments have issued various green energy efficiency directives, such as the US "Energy Star" version 3.0 TV specifications, power factor correction (PFC) specifications, etc.; consumers are also increasingly concerned about small size, multi-function, energy saving and other issues. . Driven by energy efficiency regulations and environmental awareness, power supply design is constantly evolving. This article explores the relevant power solutions for larger LCD TVs that will occupy the largest market share of full HD TVs in the future. Disadvantages of the traditional power supply scheme The traditional LCD TV power supply is mainly composed of AC-DC conversion, DC-DC conversion and high-voltage inverter. The AC-DC and DC-DC are on the same board, and the inverter is on another board, usually with the LCD panel. Among them, the AC-DC power supply part rectifies, PFC and filters the mains 110 Vac/220 Vac voltage, and then converts it to 200 V/400 V DC high voltage. Since the input voltage requirement of the conventional inverter is 24 V, the output voltage of the 200 V/400 V PFC is subjected to buck conversion to generate multiple output voltages, one of which is supplied to the inverter at a voltage of 24 V. DC-AC conversion to high voltages in excess of 1,000 V or even 2,000 V to drive CCFL backlights for LCD panels. The functional block diagram of this standard 24 V inverter LCD TV switching power supply is shown in Figure 1. For LCD TVs of 26 inches and above, a new inverter concept has emerged in recent years - LCD Integrated Power Supply (LIPS). Unlike traditional power supplies that use inverters on separate boards, this LIPS solution integrates AC-DC, DC-DC, and inverters on the same board, after rectification, PFC, and power to the mains. After filtering and obtaining a DC voltage of 200 V/400 V, 200 V/400 V is directly used as the input voltage of the inverter, and DC-AC boost is converted to more than 1,000 V and even up to 2,000 V for the LCD panel. Voltage. This eliminates the 24 V conversion section, reducing the large amount of power loss during the high voltage process of one or two kilovolts with a step-down to 24 V and then greatly boosting the backlight, thereby improving system energy efficiency, reducing chassis heat generation, and reducing The total cost. In this regard, ON Semiconductor and Microsemi have leveraged their expertise to develop high-voltage LIPS solutions for a wide range of power levels. The LIPS solution for 32-inch LCD TVs is shown in Figure 2. In terms of system board power supply, this solution uses ON Semiconductor's NCP1606 PFC controller and NCP1351 PWM controller as an auxiliary switching power supply; in the LIPS inverter part, Microsemi uses the soft-switching technology of the LX6503 phase shifting full Bridge driver, which can perform zero voltage switching (ZVS) at a fixed operating frequency. Compared to the half-bridge architecture, this full-bridge inverter solution offers significant advantages such as reduced electromagnetic interference (EMI) and power loss while improving the drive current waveform of the backlight without the need for additional power diodes on the bridge. The current specification of the four MOSFETs and transformers used in this full-bridge configuration is half that of the half-bridge structure, so that the power MOSFET can be directly driven by the isolation transformer, making it easier to implement primary-side overcurrent protection (OCP). In order to better respond to the market demand for larger size LIPS LCD TVs, ON Semiconductor plans to introduce the next generation 46-inch reference design in 2009, and the same full-bridge inverter as the 32-inch solution will be used in the LIPS inverter part. And the backlight controller LX6503, but will greatly increase the output power to drive more CCFL lamps. In terms of system motherboard power supply, you can flexibly choose ON Semiconductor's solutions according to specific design requirements, such as PFC controllers such as NCP1601, NCP1606 or NCP1631, and PWM controllers such as NCP1351 or NCP1379. This new solution uses a dedicated standby switching power supply with relays to support ultra-low standby power consumption as low as 150 mW, while component height on the board is less than 16 mm (system total less than 20 mm), supporting more fiber Thin LCD TV design. In addition, for different power requirements in different regional markets such as North America, China and the European Union, ON Semiconductor can also provide power solutions that meet the specifications to optimize the design, reduce system size and reduce costs. Advanced PFC Architecture for Ultra-Thin Full HD TV Design Today, the thickness of LCD TVs has become thinner and thinner. The latest trend is that the thickness of electronic module parts is close to 10 mm. Such a thin thickness poses a more serious challenge to the power supply design, usually requiring the use of low-profile transformers (which are particularly critical for high-voltage LIPS to consider isolation and leakage) or to connect multiple components (PFC coils) in series. The low-profile heat sink is used to mount the components horizontally, and the height of all vertically inserted capacitors is limited to 10 mm or less. In terms of PFC, LCD panels such as NCP1606 and NCP1654 from ON Semiconductor have been used to reduce the thickness of LCD TVs. To support ultra-thin designs as low as 10 mm, two relatively small NCP1601s can be used. The chip is implemented in an interleaved architecture, as shown in Figure 3. Interleaved PFCs place two smaller PFCs in parallel at a place where a single larger PFC was originally placed. The two smaller PFCs operate alternately with a phase shift of 180°, which cancels out the main portion of the current ripple per phase when the input or output is accumulated. ON Semiconductor also plans to introduce the new interleaved PFC controller NCP1631 in 2009 to provide customers with more viable options. This single-chip solution can replace two NCP1601s and is designed for extremely thin LCD TVs with a thickness of 10 mm with the same extremely low design. The solution also extends the power range to effectively reduce current ripple. Is the standby input energy consumption below 100 mW the next wave? In the future, the standby power consumption of LCD TVs will further decline. For example, with the addition of a small dedicated microprocessor, the power consumption is less than 600 mW at 50 W output power; the power consumption of the generation machine will be less than 400 mW with a dedicated standby switching power supply; if a dedicated standby switching power supply is used And add relays (thus disconnecting all PFCs and switching power supplies during standby) with energy consumption of less than 200 mW. If manufacturers want to use more "green" technology to differentiate their products, they need to further improve the design, so that standby energy consumption below 100 mW may become the next wave. Summary A liquid crystal display integrated power supply (LIPS) replaces the traditional 24 V inverter power supply, and a novel interleaved architecture reduces the thickness of the PFC module to achieve a very thin full HD TV design. This type of solution meets today's growing consumer demand for full HD TVs with 1,080 line progressive scan (1,080p) vertical resolution. In order to meet the requirements of different application markets in the world, ON Semiconductor, the world's leading provider of energy-efficient power management solutions, provides high-performance power solutions and reference designs to help electronics manufacturers shorten the development cycle of full HD TV products and make new products faster. Bring to market. Portable Battery ,Portable Power Bank,Portable Battery Pack,Portable Power Pack Zhejiang Casnovo Materials Co., Ltd. , https://www.casnovonewenergy.com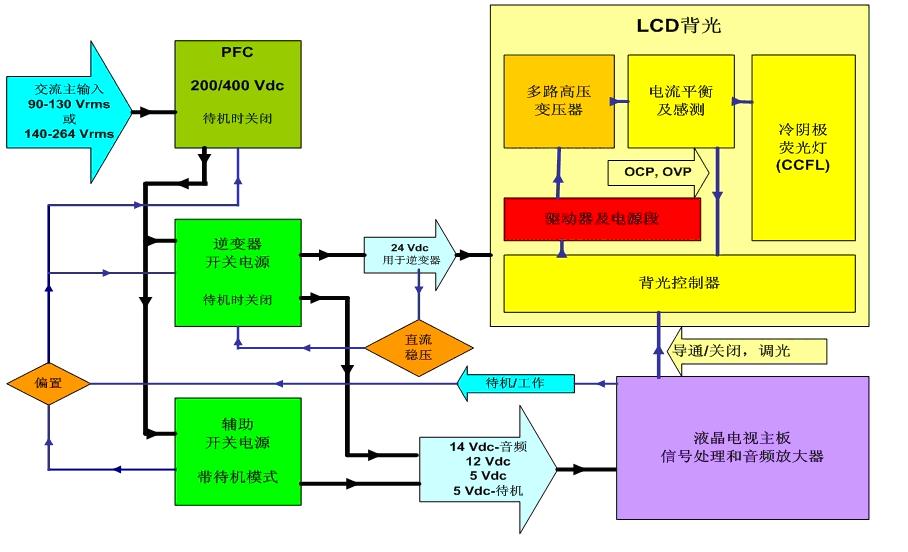
Figure 1: Block diagram of a conventional LCD TV switching power supply using a standard DC 24 V inverter.
LIPS solutions that replace traditional power solutions Currently, the traditional power supplies still account for the majority of LCD TV power supplies on the market. In order to meet various energy efficiency specifications, reduce the power consumption of larger size LCD TVs, reduce system cost and reduce the size of solutions, making them more popular with consumers, LCD TV power can be designed in a variety of ways. 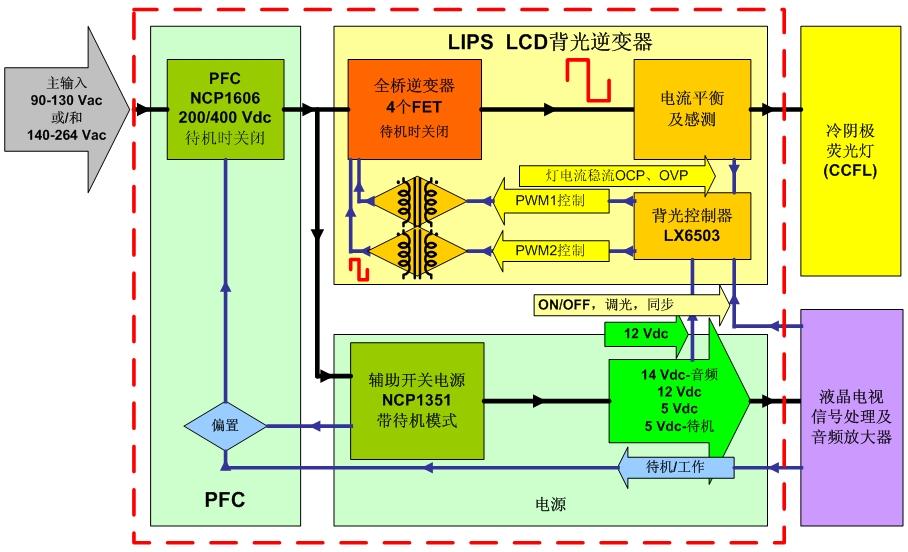
Figure 2: Functional block diagram of ON Semiconductor's full-bridge high-voltage LIPS solution for 32-inch LCD TVs. 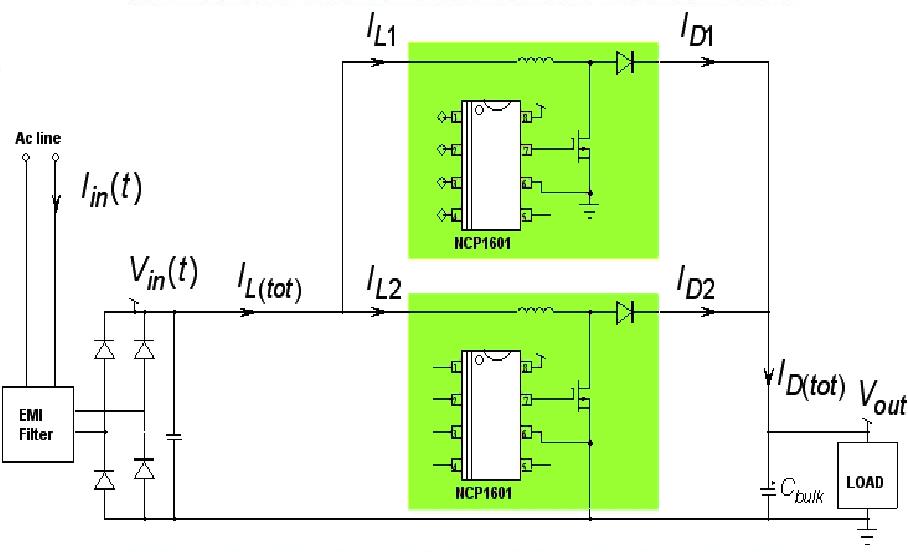
Figure 3: Functional block diagram of an interleaved PFC architecture with two NCP1601 PFC controllers.
Another focus is the standby power consumption of LCD TVs. The standard for standby energy consumption specified in the Energy Star 3.0 version of the TV specification, which came into effect in November 2008, is less than 1 W. Although not mandatory, this standard has a high market guiding significance.