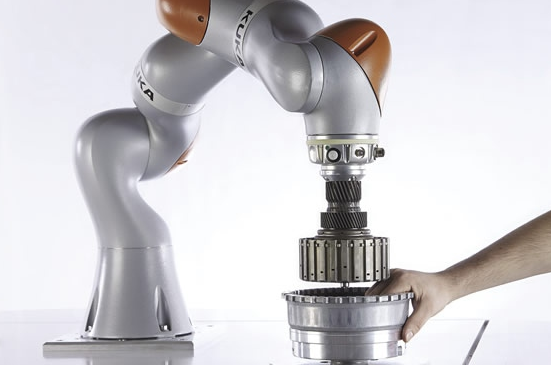
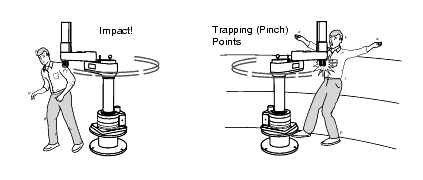
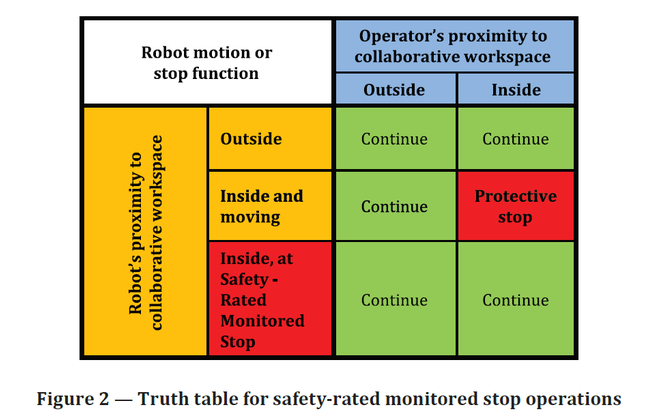
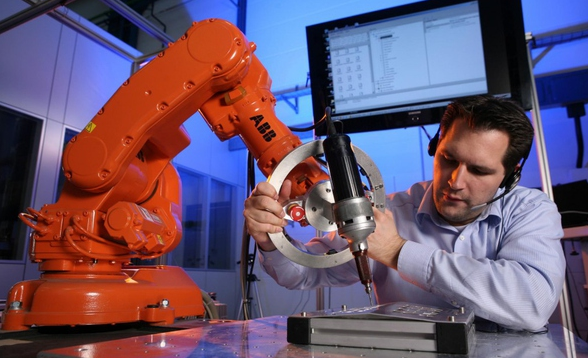
Lei Feng network (search "Lei Feng network" public number attention) by: Han Fengtao, author of this article, Yan Shi Technology (industrial robot supplier) product director. The focus of human-robot collaboration robots is "collaboration." What is collaboration? How to define this behavior? Since current robots cannot perform tasks on their own, they must install appropriate end tools and add the necessary external ancillary facilities to form a robotic workstation to function properly. So when we talk about collaboration, it's not the collaboration between robots and people, but the collaboration between robot systems and people. The concept of Robot System includes: Industrial Robot (Industrial Robot); End-effector(s); Other sensors, equipment, mechanical facilities, and external shafts are used to support robots in their missions. In any specification related to robot safety, the description of the risk assessment component is that of a robot system. This requirement is the same for a cooperative robot. For example, if a sharp knife is installed at the end of a cooperative robot for cutting, although the robot is relatively safe, the tools used are very dangerous. For a robot system, it is difficult to meet the requirements of human-robot collaboration. Most of the safety assessment of the entire robot system should be done by integrators. It should be emphasized that the cooperative robot is not unconditionally safe. Before it is used, a risk assessment must be carried out to determine the appropriate protective measures. Taking the UR (Universal Robot ) as an example, after a compliant risk assessment, it is only about 80% of the cases do not require the use of additional security measures: Around 80% of the 6 axis UR robots worldwide operation with no safety guarding after initial risk assessment. When we talk about human-robot collaboration, the first thing that comes to mind is UR, LBR iiwa, and Sawyer. This is a slender, modern-looking lightweight robot. However, human-robot collaboration is not a patent for collaborative robots. Traditional robots can also perform collaborative tasks. According to the degree of collaboration from low to high, four kinds of human-computer collaboration methods have been proposed. They are: Safety-rated monitored stop Hand guiding Speed ​​and separation monitoring Power and force limiting Traditional robots can implement 1 to 3 collaborative functions with appropriate safety controller/safety options. For the fourth kind, it is generally difficult to achieve. This is the most basic form of cooperation. When a person enters a cooperation area, the robot stops its movement and ensures a safe stop so that the operator can perform certain operations (such as installing the workpiece to be machined on the robot, changing the tools used by the robot, etc.) ); When personnel leave the cooperation area, the robot can automatically resume normal operation (Non-Collaboratively), see below: It may seem complicated, but in fact it only needs to pay attention to the two red areas in the above figure. That is, when the operator and the robot are in the cooperation area at the same time, the robot must be stationary. Manual guidance is a little more advanced collaboration, similar to the current drag teaching. In the manual guidance mode, the operator transmits a movement instruction to the robot system through a manually-operated device. Before the operator is allowed to enter the coordination area and perform the manual guidance task, the robot should already be at the safety-level monitoring stop state. The operator controls the robot to complete the task by manually manipulating the guidance device installed at the end of the robot or near the robot end effector. Manually guided operation flow is as follows: The robot enters the cooperation area and triggers a security-level monitoring stop, ready for manual guidance - after which the operator is allowed to enter the cooperation area; When the operator begins to use the manual guidance device to control the robot, safety monitoring stops the contact, and the operator begins to guide the robot to work; When the operator releases the manual guidance device, safety monitoring stops should be triggered; When the operator leaves the cooperating area, the robot system can be restored to a non-cooperative mode. If the robot system is not ready for manual guidance when the operator enters the coordination area, a protective stop should be triggered. In this mode, robots and personnel are allowed to appear in the cooperating area at the same time, but robots and personnel are required to maintain a minimum safe distance. When the distance between the two is less than the safety distance, the robot stops immediately. After the person leaves, the robot can automatically resume operation but still need to maintain a minimum safety distance. If the robot reduces the speed of movement, the safety distance can also be reduced accordingly. Speed ​​and distance monitoring apply to all personnel in the collaboration area. If the performance of the protective measures is limited by the number of people in the collaborative space, the maximum number of people allowed should be stated in the instructions for use. When this number is exceeded, Protect Stop should be triggered. When the distance between a dangerous part of the robot system and any person is less than the safety distance, the robot system should: Trigger protection stops; Triggering security-level features connected to the robot system (eg, shutting down all tools that may be dangerous) The methods available to robots to reduce the risk of violating the safety distance include, but are not limited to: Decrease the speed, then may switch to the safe monitoring stop state; Select a path that does not violate the minimum safety distance and keep moving while keeping the speed and distance monitoring function active; When the actual distance reaches or exceeds the minimum safety distance, the robot can return to normal motion. The realization of this kind of cooperation method depends on the external sensing or detection means, limited by the cost/performance limit, and the practical application is not too much. (iiwa can detect collisions or squeezing on the outside, and will not cause injury to the human body due to accidental intervention of personnel during assembly) (In the experiment, KUKA iiwa with advanced collision detection function can safely stop without stabbing after installing a dagger at the end.) The above-mentioned three kinds of collaboration methods are more like a passive means in a sense (although strictly speaking, they will not be passive), and truly let the cooperative robot achieve rapid development, and the fourth is more essential. The more advanced and safer collaboration function is to limit the ability and force that the robot itself can output, and to avoid the occurrence of injury events from the root. In addition, the above three methods do not allow a physical contact between the robot and the robot, and in this mode, intentional or unintentional physical contact between the robot system (including the workpiece) and the human body is allowed. In this mode, the operator's contact with the robot system may occur as follows: Planned contacts are part of the entire application. Unexpected contact may be caused by failure to follow the procedure, but there is no technical failure. Failure of the mode causes contact. The possible contact between moving robot parts and different parts of the human body can be divided into two categories: Quasi-Static Contact: This situation generally refers to the human body being sandwiched between robots and other components. At this point, the robotic system applies a constant force to the clamped body until it is released. Transient Contact (Transient Contact): Also called Dynamic Impact, the human body is hit by the moving parts of the robot system, and the human body is not caught or trapped by the robot system, resulting in a short-term Actual contact; transient contact depends on the inertia of the robot, the inertia of the human body, and the combination of the relative motion speeds between the two. (In the above figure, the former can be viewed as transient contact, the latter can be considered as quasi-static contact) Restricting the power and force output by the robot can ensure that people work safely beside the machine, without reducing the efficiency of the robot and increasing the application cost. This is an important function of the current mainstream collaborative robots. Related Articles: Why do we need collaborative robots? 》 This article is the author's original starting Lei Feng network, without permission, may not be reproduced!
High temperature wire, high temperature resistant wire, please don't take the safety of electricity as a bet, but the quality and credibility of your own products as a bet. If you want to find a regular cable, and find a regular manufacturer, our cables are instantly conductive, stronger and safer than others, refreshing your imagination of materials. We will spend a lifetime of continuous improvement, just to achieve the real environmental protection level of materials and reduce carcinogens. Only for health, a truly environmentally friendly material. Safety check, every product has been tested. High-precision wires have lower resistance, lower heat, and lasting and stable conductivity. Real-time monitoring of wire eccentricity and outer diameter to ensure uniform thickness of insulation layer and sheath. Eliminate the addition of heavy metals and non-environmentally friendly substances such as lead, mercury and other harmful substances. Does not contain any harmful substances to avoid adverse effects on the human body and the environment.
We eliminate mold costs and save money for customers by providing hundreds of thousands of inventory overmolding. For highly customized molded cable manufacturing projects, our advanced technology allows us to produce custom overmoldings at a price and quality level that clearly sets us ahead of our competitors.
Custom molded wire assembly, overmolded IP67/68 connectors assembling,customized waterproofing cable assembly ETOP WIREHARNESS LIMITED , https://www.etopwireharness.com
Safety-rated monitored stop
Hand guiding
Speed ​​and separation monitoring


Power and force limiting