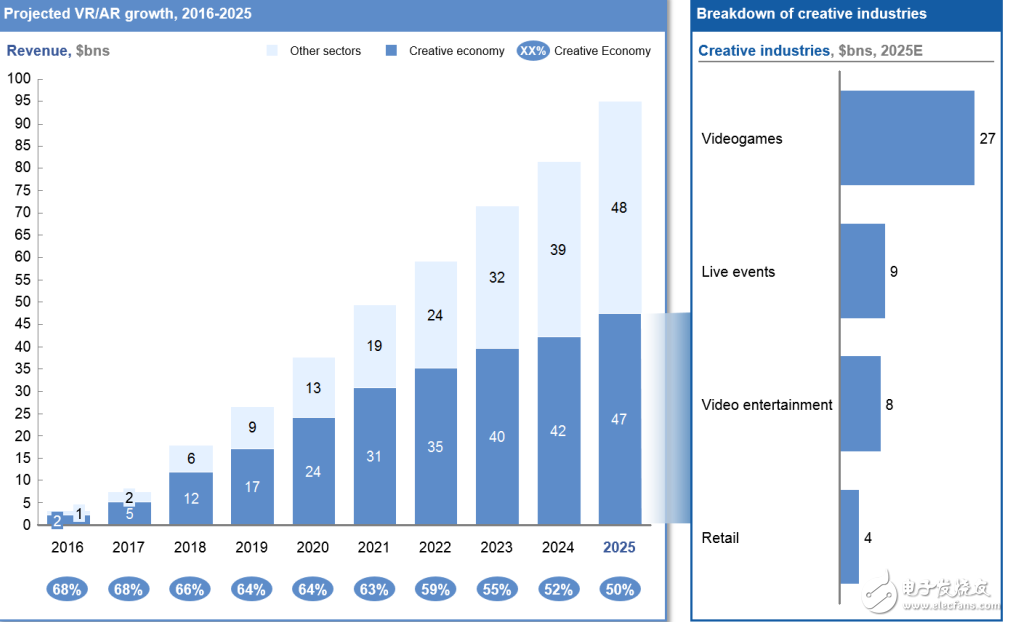
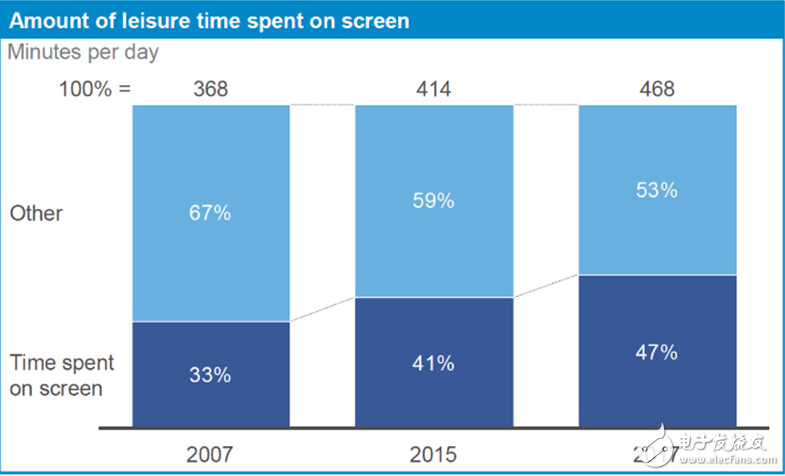
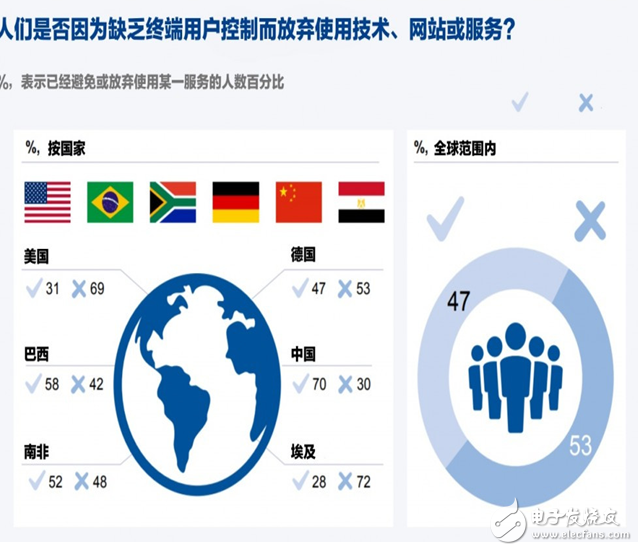
AR/VR has always changed, and the key point of change is immersive computing. The future development of AR and VR is entirely possible to replace the immersive technology of mobile computing. As a basic feature of virtual reality, it is also a key technology that users like. We can see that AR/VR is definitely bright in the future, but now immersive technology still faces social challenges. In 2016, a series of major products entered the market, and companies developing these products included Oculus VR, Sony and Google. Since the acquisition of Oculus for $2.1 billion, Facebook has acquired 11 more AR/VR companies, undoubtedly emphasizing the company's view of VR and AR as the next technology frontier. The massive investment and acquisitions of technology giants show that these technologies will increasingly be combined with our platform for consumer content. According to Goldman Sachs' latest forecast, by 2025, AR and VR are expected to reach a market of $95 billion. As shown below, the current largest demand for technology comes from the creative economy—especially games, live broadcasts, video entertainment, and retail—but, over time, broader applications will involve healthcare, education, military, and Real estate and other industries. AR/VR changes the way you create and experience content: 1. From "seeing" to "deep experience" Artist and technical expert Drata Kataoka said that AR and VR will provide a new creative medium - "the artist's dream to build the world with pixels." This means that the world is expanded with ever-expanding concentric circles and thus provides an unprecedented The technology of immersion and experience will replace the linear equipment of the past. This will be a disruptive initiative: users no longer “see†the content, but are exposed to the expanding virtual world and find themselves in the center of this virtual world – here is the “immersive†nature of technology. . Eugene Chung, founder and CEO of Penrose Studios, said: "Since 1896, we have been using the same flat screen media. VR/AR uniquely provides a sense of presence and immersion, it is a brand new art Form, a new way of experience." 2. Reduce production costs “Virtual Prototyping†allows us to reduce the iteration time and cost of product development, while also improving the quality of the end product. For example, a design company saved $50,000 in cost for a certain airline customer by using VR prototyping, eliminating the need for two physical prototype cycles and eliminating the time required to assemble custom samples. The widespread use of virtual prototyping will enable companies to reduce the number of prototypes required and greatly reduce the time from concept design to production and commercialization. While traditional technologies can also allow companies to prototype, immersive technology allows designers to interact more directly with their prototypes in a VR or AR environment. This means that immersive technology provides greater precision in design, providing a higher quality, lower cost end product that is not possible with traditional prototyping. 3. New creators have low barriers to entry Immersive technology also allows small companies to produce high quality content at a lower cost. There are techniques that can process 360-degree images in a matter of hours—this process often takes several days before the technology appears. And, filmmakers can use the technology with less budget. Similarly, smartphones and apps make mobile photography no longer exclusive to professional photographers and enthusiasts. We can expect that AR and VR will open new miles of innovation for all of us. 4. Tools to enhance empathy and awareness Immersive technology may also enable us to more immersively experience global issues, such as humanitarian crises, so that people who are thousands of miles away are like being in the scene of suffering and evoke deep sympathy. Artist and director Lynette Wallworth believes that AR and VR "provide a real sense of experience that other media can't reach." Although some believe that the increase in digital media consumption may reduce people's compassion. Many artists working in the AR and VR fields believe that this medium will become the “ultimate sympathy machineâ€, providing society with other groups and identity perspectives. Gabo Arora, founder and president of LIghtshed, the creative director and senior consultant of the United Nations, explained: "You are mining a new grammar that tells stories and emotions." If this positive view is proven to be effective, our world may be true. It will become more creative and more human. VR and AR also have great prospects for providing an immersive learning experience. In addition to instant gamification learning, VR and AR biosensors have been used in the field of mental relaxation, allowing one to use the brain for the first time in life. Tan Le, CEO of EmoTIv, said: "Immersive technology is a form of brain enhancement that links our biological systems to digital devices." Talent competition limits development In addition to technical challenges, another potential factor hindering the rapid development of the AR/VR field is the lack of talent to keep up with the pace of development. This is a “new†field, so there is no data to show the gap between talent supply. However, there are still clues to know a little. For example, data from the United States show that in the second quarter of 2017, the industry's demand for freelance workers with VR expertise grew much faster than the demand for free workers of other skills, 30 times that of the same period last year. Similarly, a survey of more than 200 Canadian companies engaged in VR projects revealed that VR will face a serious shortage of talent, which will eventually lead to “increased business mergersâ€. 1. Strategically cultivate local talents The government should develop a strategic plan to capture emerging technology talent to ensure that its country is at the forefront of the next computer development. China is an example of early action, and the vice president of Perfect World said: "The Chinese government has provided a lot of support for the VR industry." For example, Zhongguancun in Beijing provided nearly $1.45 million in funding for major companies to further develop the VR industry and position the region as the next global technology center. Other areas, including the VR Village in Beidouwan, Guizhou Province, also provide funding for content development and investment. By 2019, Beidouwan is expected to produce 1.5 million pieces of VR-related hardware and more than 500,000 software content transactions – and provide 3,500 new jobs in the process. 2. Introducing foreign talents The government can also actively invest in immersive content. A survey of 500 AR/VR professionals in 2016 showed that nearly 50% of companies are using their own personal funds to develop their companies; less than 8% of companies say they have “other†channels of funding, including government sponsorship . Considering that VR production costs can reach hundreds of thousands, forward-thinking policy makers are pushing the subsidy policy to attract VR talents from all over the world, and make great strides while protecting the development of the domestic industry. For example, in France, the government-backed CNC Fund (CNC Fund) funds VR/AR producers and works with local teams to produce content that covers development and production. In a recent case, the fund provided 40% funding for a VR short film costing about €500,000. CNC is also authorized to provide up to a 30% tax rebate for all or part of the projects initiated in France and initiated by non-French companies. Are these methods working? Although its impact on VR content remains to be evaluated, this policy seems to be effective in supporting French “traditional†film production. A year after the implementation of the policy, a total of 31 projects from 8 countries were launched, compared to 4 projects in the previous year. These projects, including blockbusters such as The Pirates of the Dream, are expected to cost about €119 million in direct spending in France, involving 450 days of filming – compared to the year before the launch of the policy, direct spending was only 7.4 million euros. The time is only 84 days. Considering the initial stage of development of VR, it is difficult to say whether these benefits can really be transferred to this emerging industry, but the attraction of this mechanism to creators is beyond doubt. Immersive content is more personal, but costly Software designers are increasingly focusing on keeping users on their websites and applications because their business models are increasingly relying on collecting personal data to produce personalized content. Adam Alter, associate professor of marketing at New York University's Stern School of Business, described the strategy as a “powerful big data drive†approach: “The company will inevitably A/B test different features of the product and iterate over it.†In addition, there is sufficient capital The company will "form up a team of psychologists to get users based on the latest information." In fact, evidence from the past decade shows that while our overall leisure time is increasing, we spend more and more time on screen-based devices. The key driver of this shift is the use of interaction as a major success indicator for digital technology. The more time we spend on the device, the more data we can collect about our interactions, which in turn leads to more targeted products; as immersive technology becomes mainstream, this enhanced cycle is likely to accelerate significantly . As a result, the content we experience in immersive technology will become more and more personalized. This will be reflected in a variety of ways, and the biggest benefit is the advertising industry. 1. Advertising is more targeted Thanks to our personal data, advertising has become more and more personalized. In the context of immersive technology, people have created a new term, "gaze rate," which is used to describe the efficiency with which an enhanced or virtual ad captures the user's attention. Companies such as ReTInad also provide user behavior tracking analysis on VR/AR devices to increase the conversion rate of ads and how users interact with content. So far, this new ad type has shown excellent user interaction, which is 30 times more efficient than mobile advertising. 2. Deeper interaction may have a negative impact on health and privacy The motivation to attract our attention brings two challenges. First, our health is at stake: Obviously, non-screen activities are healthier. A longitudinal study of major social media found that there is an inverse relationship between social media interaction and personal health, indicating that “online and offline activities should be balancedâ€. In the United States, teenagers who spend 6-9 hours a week on social media think they are 47% more likely to be unhappy than those who spend less time on social networks. Second, the lack of control over personal information may jeopardize users' long-term adoption of new technologies. According to a report by the World Economic Forum, 47% of the population in six countries have stopped or avoided using a service due to inadequate user control, especially in China, which is as high as 70%. This suggests that user privacy and data control are top concerns for consumers. Considering the deeper data tracking functions in immersive technology, such as eye movement and facial expression tracking, and touch data (related to touch), personal data at risk brings more privacy concerns than ever before. time. Suggestions for the user design center 1. Regulatory framework Privacy issues related to traditional media have emerged in immersive content. If developers are unwilling to provide clear and acceptable terms of use, regulators must be involved in personal protection – many jurisdictions have already taken this action. The regulatory framework already implemented in traditional digital technology provides the best reference for how to monitor future immersive technologies. In the European Union, the General Data Protection Regulations (GDPR) will come into force in 2018. The law not only stipulates that data collection must first obtain user consent, but also forces the company to clear personal data as required. In the event of a violation, the company can face up to 4% of the company's global annual turnover. In addition, the concept of “data portability†is included in the bill, which allows users to use data across platforms – a measure that effectively motivates innovative startups to compete with large companies. Of course, other similar immersive technical regulations are also evolving. 2. Provide personal data sovereignty to users Analysis shows that major VR companies are already using cookies to store data, while also collecting information about location, browser and device type and IP address. In addition, communication with other users in the VR environment will be stored, and all data can be shared with third parties and used to personalize products for marketing purposes. Concerns about the collection of personal data have spawned temporary solutions to provide a buffer between individual users and businesses. For example, the Electronic Frontline Foundation's Privacy Monitor is a browser plug-in that automatically blocks hidden third-party trackers and allows users to customize and control the amount of data they are willing to share with online content providers. A solution like this that returns control of personal data to the user is also applied to immersive technology. But for now, the data protection tools available to individuals who are both uncomfortable with data collection and eager to explore AR/VR are primitive and limited: they can only use "offline mode" or separate files for new devices. 3. Manage consumption There are also short-term measures presented by the cessation mechanism to address the problem of overuse. According to reports, in the United Kingdom, 71% of young people support the use of warnings once the length of use approaches or exceeds the health limit. Services such as unGlue allow parents to set filters on the types of content their children are exposed to and set usage time limits for individual apps. All of these measures can also be applied to immersive technology and as a supplement to actual regulation. For example, South Korea’s “Closed Act†prohibits teenagers under the age of 16 from accessing the game site between 12 midnight and 6 am. This policy is enforced because it associates personal data (including date of birth) with the citizen's resident registration number, and the user must submit their resident registration number when registering for the online service. These methods are not absolutely reliable: for example, a child with a chance can continue to “borrow†other adult devices to solve the restriction problem after a few hours. Further research is obviously necessary, but we believe that the long-term solution should be better design. 4. Rethink the success indicators of digital technology As companies continue to develop applications that use immersive technology, they should transition from using metrics that measure user engagement to metrics that balance user satisfaction and health promotion. Alternative indicators can include the customer's recommended score for the software—that is, the level of social contribution and satisfaction based on the software service, the user, and even the regulatory agency, who are willing to recommend it to their friends. However, the real challenge is to find measures that meet business policies and user goals. According to Tristan Harris, founder of TIme Well Spent, “We have to face the current imbalance so that we can find a solution.†In fact, improvements in user experience and business opportunities do not always run counter to one another. Subscription-based services are one of the examples: YouTube Red will clear ads for paying users, as well as SpoTIfy Premium. Users can enjoy an ad-free experience for a fee, and content developers don't have to pay any cost because they can earn revenue from paid subscriptions. Immersive technology has a lot of work to do in order to make the interaction between users and content and media more enjoyable and fulfilling. And the realization of all this depends on the technical design that puts the user at the core of its value proposition.
The utility model relates to a medical atomization treatment and humidifying device belonging to the technical field of medical equipment and household appliances.
Professional Medical Atomization manufacturer is located in China, including Medical Vape,Dose Control Vape Pen,Supersonic Wave Vape, etc. Medical Atomization,Medical Vape,Dose Control Vape Pen,Supersonic Wave Vape Shenzhen MASON VAP Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.cbdvapefactory.com