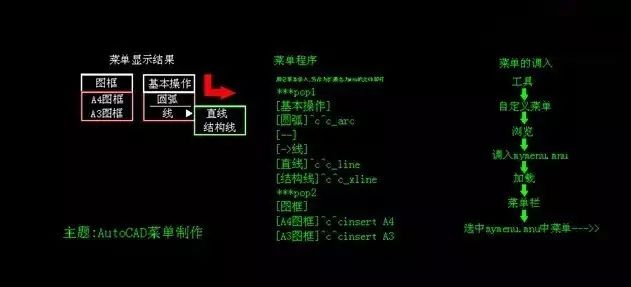
Prepare knowledge In the avatar, if there is no special explanation, it is in millimeters. Smoothness determination: Tool/option/display/arc and circle smoothness is 20000. Note: Maximum Right-click function cancel: shortcut menu does not appear in Tools/Options/User System Configuration/Drawing Area Password Settings: Tools/Options/Open and Save/Security Options below Object Capture Settings: Tools / Sketch Settings / Object Capture - All Selections UCS icon visibility: view / display / UCS icon / (on / off) Relative coordinates: plus @ Relative Cartesian format: @x variable, Y variable Relative polar format: @length<angle The angle is the angle with the horizontal positive direction: The horizontal direction is "0" degrees, counterclockwise is positive, clockwise is negative There are two sizes: the shape ruler and the positioning ruler. When drawing a line, U is the undo step C is closed, or you can press CTRL+Z to cancel to the last operation. Enable object capture shortcuts (F3) Orthogonal mode shortcut (F8) The F2 key switches between the command line window and the drawing window. AutoCAD has no special requirements for color Choose three common methods: 1) Drag the window selection from left to right, you have to frame to select 2) Drag the window selection from right to left, you can select it if you touch the object, and you can also select it in it. 3) Click In the operation of AutoCAD, in general, the right mouse button is equivalent to the Enter key. After the operation is completed, press the right button again to repeat the last operation. Three-button mouse The middle button scrolls outward to zoom in and scrolls in to zoom out Plane part one [Two columns of toolbars, except text, tiles, multi-line] Toolbar operation: Drawing toolbar (equivalent to the drawing menu) Straight line (L): full name (line) Specify two points on the screen to draw a straight line. Relative coordinates Or when the orthogonal mode is on, directly drag the actual distance to control the direction. Construction line (XL): full name (xline) H is horizontal V is vertical O is offset A is angle B is an equal angle. Polyline (PL): full name (pline) First specify a point on the screen and then have the corresponding prompt: Specify the next point or [Arc (A) / Half Width (H) / Length (L) / Abandon (U) / Width (W)]. Can be set as needed. The "circle" specifies the width to draw any angle arc; "half width" refers to the half width of the polyline, that is, if the height of the line is 10, then 5; "length" gives the corresponding value, then draw the corresponding length Polyline; "abandon" means giving up one operation; "width" means the width of the polyline Polygon (pol): full name (polygon) The drawn polygon is a regular polygon, and the number of edges can be set by itself. E: Draw a polygon according to the edge. You can also use the outer and inner joins to draw a regular polygon according to the radius of the circle. Rectangular (REC): full name (rectang) The following tips appear after clicking the Rectangle tool: Specify the first corner point or [Chamfer (C) / Level (E) / Fillet (F) / Thickness (T) / Width (W)] The "chamfering" is to cut off the two sides of the 90 degree right angle. Become a bevel. "Elevation" is the meaning of space can be displayed in three views, the elevation is relative; "rounded": that is, the four right-angled sides are rounded into a radius of X; "thickness": the meaning of space The "width" can be expressed on the Z axis: the concept of a flat space, which refers to the width of the four sides of the rectangle. Arc (ARC or A): The default is to draw a circle with 3 points, the direction of the arc is counterclockwise, and the radius of the arc is given to a negative value. The following options are available in the drawing menu: Starting point, center of the circle, end point; Starting point, center, angle; Starting point, center, length; Starting point, end point, angle; Starting point, end point, direction; Starting point, end point, radius; Center, starting point, end point; Center of the circle, starting point, angle; Center of the circle, starting point, length; Circle (C) full name (circle) The default is the circle radius [diameter] to draw a circle. There are options in the drawing menu: two points, three points, cutting radius, and cutting the circle. Cloud line (revcloud) is used for marking (not important) Spline curve (SPL) full name: (pline) After confirming each point with the left button, three carriage returns: the first break, the second start tangent direction, the third end tangent direction Ellipse (EL) full name (ellipse) uncommonly used. Give the total length of the long axis first, then give half of the short axis. Or draw in the center: half each of the long and short axes. Ellipse arcs are not commonly used. Used to draw elliptical arcs Point (P) full name (point) The point tool can't press the right button to confirm the exit. To exit, you can only press the ESC button. There are the following drawing operations: Format: dot style The size of the point is 10% relative to the ratio of the screen. The icon outside is equivalent to multiple points. During operation, press ESC to exit. Single point: in the drawing menu, click on a point to exit Fixed-point aliquot (DIV) of points: divides an object into N equal parts by point Pointwise equidistance (ME) of points: Mark an object by a long distance For the division of the closed path, the N equal division is N points; the open path is equally divided, and the N is divided into N-1 points. Note: The operation of the point is different from the operation of other tools. Repeat the last operation after exiting to return to the last time you want, unlike other drawing tools that have a joint menu. Pattern fill (BH) full name (bhatch) Must be a closed object to fill At the beginning of AR, there are more buildings. ANSI American National Standard ISO International Standards Organization standard Be sure to preview the ESC or right click to return Edit hatch: Modify II: second icon After the profile is filled, the characteristic can be matched to MA without decomposition. Do not break the fill pattern as much as possible for editing Three advanced settings for pattern fill: External meaning, which area to click, which area to fill Note: Ignore padding, ignore it inside, and calculate it inward. Area (REG) full name (region) Premise: End-to-end closed body Introducing the concept of point line body Converts a closed object that is connected end to end from a wireframe to a face, enabling line-to-face conversion. The first time will be a bit slow Extension to Boolean operations: Call up entity editing, three forms of Boolean operations: union, difference, intersection, only the area can be Boolean Modify the toolbar: Delete (E) full name (erase) Used to delete the object, click delete to enter ALL on the command line to delete the drawing area so the object; the default is to delete the selected object Copy (CO) full name (copy) Used to copy objects, the default is to copy selected objects; specify the base point to move the copied objects to another location. Can be moved to the actual size: three cases, only one copy, multiple repeat copy, distance copy, relative coordinate copy Mirror (MI) full name (mirror) Used to copy an object that is symmetrical with the source object. By default, two lines are specified to define a mirror line. Features: the corresponding points are vertically divided Mirrtext (mirror variable control command): give 1 full mirror, give 0 graphics image, text is not mirrored Offset (O) full name (offset) To achieve the offset of the object, first offset the size, and then press the right button to exit after the offset is completed. Array (AR) full name (array) key content An array of objects is implemented, which has a rectangular array and a circular array; in the form of a dialog box: Rectangular array: set n rows and m columns, and then give the row offset value and column offset value, divided into four quadrants Ring array: First determine three elements: center point, total number of items, fill angle, there are three options Mobile (M) full name (move) Realize the movement of the object, can operate on the actual size Extension to grip control Rotation (RO) full name (rotate) Realize the rotation of the object, refer to rotation and free rotation; orthogonal open is calculated by 90 degrees, Scale (SC) full scale (scale) Realize the scaling of the object, the default is scaling, the application of the object properties changes, the application of the R reference Stretch (S) full name (stretch) Must be selected from right to left, and only local can be selected. Selecting a point will operate on one point. Selecting two points will operate on two points. Selecting all points is equivalent to moving the tool. Divided into accurate stretching and random stretching, reference stretching Trim (TR) full name (trim) Used to trim the object, the operation method, click the trimming tool and press the right button to confirm. Then use the left button to trim, skill operation: (one-time trim) point trim, select the dividing line, confirm, input F, then select two points, propose a straight line, be selected, all trimmed Independent segments cannot be trimmed Space Trim: Select Trim, right click, input P (projection) has two options, N, must be true intersect, U projection to XY plane trim, V current view projection trim. Extension (EX) full name (extend) Used to extend an object, first select the extended boundary, confirm and select the extended object. Break at the point (BR) full name (break) Interrupt an object at a point, use the left button to select the object and then use the left button to point to the object. The point in the point will be used as a break point, inaccurate, basically no application. Interrupt (BR) full name (break) Interrupt an object, interrupted at two points, inaccurate, basically no application Chamfer (CHA) full name (chamfer) Remove the two sides of the object by a distance; have the following tips: ("Trimming" mode) Current chamfer distance 1 = 0.0000, distance 2 = 0.0000 Select the first line or [polyline (P) / distance (D) / angle (A) / trim (T) / mode (M) / multiple (U)] The "polyline" refers to an operation on an entire object, such as a rectangle, which can be used to dump four sides at a time; "Distance" sets the distance of the chamfer, the first side and the second side; "Angle" sets the chamfer by the angle; "Pruning" determines the chamfering mode, whether to trim; "Method" determines the chamfer Way, whether it is inverted or angled; "multiple" can be used if there are multiple identical chamfers Rounding (F) full name (fillet) Pour the angle formed by the two sides of the object into a rounded corner with the following tips: Current setting: Mode = Trim, Radius = 0.0000 Select the first object or [polyline (P) / radius (R) / trim (T) / multiple (U)] "Multi-line" refers to the operation of an overall object, such as a rectangle, which can be inverted at four times; "radius" sets the radius of the rounded corner; "trim" sets the rounding mode; Can be used when there are multiple identical roundings Decomposition (X) full name (explode) Decompose a whole object into a plurality of independent objects, that is, decompose into lines; if the body is to be decomposed into lines, it is decomposed twice, that is, the body is decomposed into faces and then decomposed into lines by faces. Plane part two Template file creation (DWT file) saves after setting the drawing environment How AUTOCAD graphics are made into images: file/output Optional .wmf/ .bmp The 2002 version must turn the background into white. There is no need to change the background color after 2004. Text: Single line: DT, you must press Enter when you enter a single line. In this case, the right button cannot be equivalent to Enter. Multiple lines: T or MT (new toolbar) Font selection: Chinese characters: Song style, imitation Song body default font (txt) is generally not commonly used It is recommended to use the simplex.shx font for standard text (simplex.shx does not recognize Chinese characters, txt.shx does not recognize) Engineering text: Select the simplex.shx font to select, tick the large font, select gbcbig.shx font to lose Chinese characters and numbers. Input for five special symbols: Diameter symbol (%%C), plus or minus sign (%%P), degree (%%D), %%u<content>%%u underlined, %%O<content>%%O With a line, you can add both underline and underline Text overlay: The text should be tilted 30 degrees When facing, the right side is tilted to the right, upper and left, tilted to the left When you type again, the last text you entered last time will be selected, you can ignore it. Tile: (B, W) full name (block and WBLOCK) First, the block production 1), the icon on the toolbar is equivalent to the input B. The tile created in this way only exists in the current file, and the replacement between the tiles cannot be realized. It can be called by the design center CTRL+2. 2), W to make a tile, this tile can be placed in a specified directory, can be easily called, and can achieve mutual replacement of tiles Second, the insertion of the tile: 1), insert --- block, browse, find the tile name 2), minsert can achieve array insertion of tiles Third, the replacement of the block, the operation steps: 1), enter -i at the command line, enter 2), replaced tile name = replaced tile name, enter 3), enter Y, enter, that is, confirm the tile redefinition, achieve replacement 4) Press the ESC key to cancel the insertion of the tile and only implement the tile replacement. Fourth, the definition of attributes: The attribute is the information attached to the tile. It must be combined with the tile to implement its own function. When the tile is inserted, the prompt information is input. Attachment: Determine the replacement path of the tile, determine the search path of the tool/option/file/support project file after determining the directory where the tile is placed, and click “Add†to find the directory where the tile is stored. Block replacement can only be achieved if the search directory meets the requirements. The definition of the tile attribute: Drawing - block - defining properties Edit properties (for text operations that define properties) If you specify a point on the screen, the entry of the attribute is displayed by the command's equation. If it is inserted at the origin, it will be prompted in the form of a dialog box. Tile example: Supplementary note: If you want to use the backup file if you want to use the backup file, you can directly rename the backup file to .dwg. Multi-line (ml) multi-line editing (mledit) Architectural drawings are generally divided into two categories: architectural construction drawings, interior decoration drawings Multi-line icon loading: right click on any floating toolbar - toolbar - custom - command - drawing - multi-line Multi-line width control, the default width is 1. Because N times of 1 is N. The number of lines in a multi-line can be changed: Format - Multi-line styles When building an architectural drawing, the multi-line is generally set to three. Multi-line proportional control - for the thickness of the wall. The general ratio is: 120 240 360 480 and so on. There is an alignment setting when drawing multiple lines: there are three alignments - up, down, and none. Select "None" during the drawing process. The mouse is aligned in the middle. Up and down are generally not used. Multi-line cannot be trimmed without blasting. (Note: you will not be able to recover after the explosion!) The middle line can be deleted after the building wall painting is completely completed. Use: Tools - Quick Selection - Color Selection If you can't choose by color. Two reasons. First: the color code is not correct. Second: multiple lines are not broken down. The size of the doors and windows in the building: windows generally have 1.5X1.2X0.12 and so on. The door generally has 0.04X0.9X2.0, unit: m) There is also a drawing of architectural drawings - if all the size of your house is to go to the home with a ruler. Then draw the interior wall first. Then use the offset to do it. Layer application: (mainly assigning objects) Layers are turned on and off: all layers can be turned on or off; layers are not displayed, not drawn, but participate in calculations. Layer freeze: The current layer cannot be frozen, and other layers can be frozen. Locking the layer: The locked layer cannot delete the object, but you can draw the graphic into it. Graphics that have not been modified can change as the layer transitions. Objects in the layer cannot be deleted. To delete, you must delete the content in the layer before deleting it. 0 layer cannot be deleted, and the defined point layer cannot be deleted. The current layer cannot be deleted. Layer classification: Building: floor plan, furniture, signage, each room Machinery: dotted lines, dotted lines, graphics, labels In general, the settings of the layer: Drawing, text, dotted lines, dashes, frames, labels Note: Single line loading: dotted lines indicate invisible lines, dotted lines indicate symmetrical lines, adjustment of line type ratio Note: If you want to select all objects of a layer: Tools - Quick Selection - Layer Title bar Small 110 big 180 Line spacing is 7 or 8 mm Title bar content: design, drawing, review, approval, standardization, map name, scale, map number, frame, view, etc. Use of some accessibility features in AutoCAD: Query function: Area calculation: If there are multiple lines, you must first make one with the boundary. Then calculate again. The calculation of the first rule graphic area: tool - query - area and then find one point at a time. Calculation of the second irregular graphic area: tool - query - area and then enter "O" Calculation of area increase reduction: first calculate by adding mode, then use subtraction mode to calculate. Distance: Only the distance of the straight line segment. Calculation of the distance of the arc: Available features to see the arc length. Another is "query" --- "list display". Note: Handle: is a code given inside the computer, not the same. Representation of the label of the arc length: in general, artificially add an arc to the label Mass calculation: The characteristics of the area or mass, calculated in milligrams. The default density is calculated as the density of water CAL: Calculator Point coordinates: (absolute coordinates can be viewed with object properties) Time: can query the time of opening the file Auto save: Tools - Options - Open and Save Command: savetime The use of the PE command (open path) becomes the overall format: PE selects the object right J [closed path becomes the whole] Three methods: PE, area, boundary Passwords can be added to AutoCAD: security options, status, and many items are listed. Fill (system variable for filling display) can be input: ON, OFF. Re (refresh screen) When the file is opened, there is no dialog box when the system variable (filedia) of the dialog box is displayed to "0", and a dialog box is given when "1" is given. Sketch [hands-free line (meaning of sketch)] Parity padding of Solid graphics: odd points are connected to odd points. Even points are connected to even points (no use) Trace equal width line (less applications) Ray ray donut ring Abbreviation for ltscale linear proportion (control of overall linear scale) Mid midpoint capture, CEN center capture tan point capture, etc. Hyperlink CTRL+K application. Insert - Hyperlink hyperlinks can be copied. Open the context menu when using a hyperlink. Labeling: Labeling is an important part of a flat graphic. [with annotation toolbar] Line type annotation: The default is to find the first point and then find the second point. You can click the right mouse button once to appear a small square and you can easily mark it. The marked data is the variable of X and the variable of Y. Alignment: The distance marked is the true size. Coordinates: Turn on the orthogonal function when making coordinate labels. The coordinate value marked in the horizontal direction is the coordinate value of the Y axis (absolute coordinate value). The coordinate value marked vertically is the coordinate value of X (absolute coordinate value) Note: The origin of the coordinate system can be freely changed. Radius, diameter: used to mark the radius and smuggling of the arc and arc. Arc: The most used is the radius dimension. Circle: Available radius or diameter. casual. Angle: An infinitely long line cannot be angled. Baseline labeling: It must be marked with one label; the left point of the first label is based on the left and the right side of the first label is based on the right. Continuous labeling: There must also be a prerequisite. Then there is a one-to-back mark. Lead: A line that is easy to label. The movement of the dimension text to be done by the leader does not affect the leader. After drawing the lead, press the Esc key. Tolerance: The amount of tolerance can be given according to actual experience or by checking the manual. Geometrical tolerances: (shape, position tolerance) (Note: tolerances are specifically described in the book. You can buy the materials yourself to see) The tolerances cannot be decomposed. Belongs to an external reference class. If you want to modify the available edit text to modify. Center mark: Add a mark to the center of the circle. The default size is 2.5 mm. Tilt: Tilt the label, give the tilt angle after selection Align text: There are five options including: (default, angle, left, center, right) Style: You can change the style of the label. Label style: The following buttons are available on the first page of the Dimension Style dialog: Set to current: Set a dimension style to current. New: Create a new dimension style. Edit: Modify the label style options. Modify directly in this diagram so the label changes Alternative: Replace some of the options in the current dimension style with another option. But do not change the marked object. Compare: Compare the options in the two dimension styles. List the different options. (A dialog will pop up.) Click the New button to go to the next dialog. The tabs inside are: New style name: specify a new style name Basic new style: Use which dimension style is the basic style. Used for: for all labels or... Filling in the point will continue to set the new dimension style for the next step. The next level dialog is the same for point modification and substitution: the tabs are: Lines and arrows: The properties of the lines and arrows of the labels are changed in this tab. Text: This tab is used to edit the label text attribute Adjustment: Adjust some settings for the annotation. The focus is on: global scale Main unit: Set the unit of the label and the accuracy of the label. And the scale factor of the label (Note: the scale factor cannot be changed casually.) Conversion unit: such as hook. The converted units of the label will be displayed. (converted before metric millimeters and feet inches) Tolerance: Set the tolerance. Generally not used. Note: Control of the scale: the control of the global scale. When the frame is magnified N times, the global scale is given N times. Conversely, if the frame is reduced by 1/N, the global scale is given to 1/N. Tolerance symbol: Formula for public relations: Basic: dimension H tolerance height S deviation Note: H and S must be uppercase. 1:1 graphics: H can be set between 1.25-1.5. 1:N graphic: H is set between 1.25N-1.5N. 1:N graphic, the global scale is set to N. The opposite is also set. As long as it is accurate drawing, it must be drawn according to the actual size. The frame is magnified N times to frame the graphic. Then the scale of the graph is 1:N. Update: Update the annotation, no application Update associated annotations: Update associated annotations, no application The dimension line and the text are a whole. To move the label's text, you need to break the label and move it. Or use text alone to enter. If the words are piled together after the labeling, they can be blasted and then moved to adjust the position. The multiplication sign in mathematics in the annotation can be replaced by an uppercase "X". Positive isometric side view Three View: The plane, the facade and the side are perpendicular to each other. The front side is the main view, and the left view can only be determined after determining the main view. Which surface parameter is more common will generally be which side is the main view, then other views. Three-view structure: Main view and top view are long alignment The main view and the left view are high and flat The top view and the left view are equal in width. Chinese standard: the left view is on the right and the right view is on the left. Graphics generally consist of four views: First, the normal orthogonal view Second, full section view Third half cut view Fourth, partial section view Two ways of drawing avatars: First corner painting Triangle painting Axonometric Axonometric definition: 1. Enter the Axonometric System: Tools - Sketch Settings - Capture and Grid - Select "Isometric Capture". 2. In the process of drawing the isometric drawing, in general, the orthogonal mode is turned on, and the offset and mirroring cannot be used directly. The F5 key can enter a cyclic switch between the top, right and left sides. The points shared by the three sides have a difference of 120 degrees between the straight lines of the corner points formed. The three sides are perpendicular to each other. During the drawing process, three sides are continuously switched to form a three-dimensional plane solid figure. 3. The axonometric drawing is a three-dimensional structure expressed by a planar figure. The circle in the isometric drawing system must be drawn by the ellipse. After the ellipse icon is clicked, input I, determine the center of the circle, and then give the radius to draw the equiaxed side circle. 4. The chamfer of the side view can be directly inverted; when rounding, the rounded center must be determined, the side circle of the shaft should be drawn, and the rounding can be formed by trimming. 5. Marking of the axonometric map: For the linear annotation of the village, generally use the "alignment" label, and then apply the "marking" "-" "tilt". After the point is marked, input the formal negative 30 degrees according to the direction to form the label veneer. For the labeling of circles and arcs, you must make your own. The direction of the axonometric map: Upper north, lower south, left west, right east (view of view, southwest from 45 degrees). Some tips in the drawing of the axis side: Thread drawing: Drawing of the explosion map: Drawing of regular polygons in an isometric drawing: using the fixed number of points to do Rounding chamfer of the isometric drawing: AutoCAD's rounding chamfer is divided into three types: plane, axis, and 3D. The chamfer of the isometric drawing is controlled by D and can be directly inverted. Rounding: You can't directly pour it. Use an ellipse to do it. Draw an ellipse by looking for the center of the circle, then trim. Labeling practice: After labeling, mark again - tilt positive or negative 30 degrees, the circle and ellipse labels must be done with leads. The axonometric drawing is a quasi-stereoscopic figure; the stereoscopic drawing is a quasi-axial drawing graphic Decompose the 3D graph and decompose it twice. The first time is divided into faces by the body, and the surface is subdivided into lines. Drawing of accurate size isometric drawings The tangent of the big circle and the small circle in the isometric drawing, first find the tangent point, extend it after drawing, and then connect, find the midpoint, and draw one. a little perspective Two-point perspective Oblique biaxial mapping Three-dimensional part UCS: User (Coordinate) System (Coordinate) System WCS: Word (Coordinate) System (Coordinate) System UCS type: 1. The origin UCS can place the origin of the coordinate system without changing the three-axis directions of X, Y, and Z. 2. Z-axis vector UCS: The first point determines the origin, and the second point determines the positive direction of the Z-axis. 3.3 point UCS: The first point is the origin, the second point is the positive direction of the X axis; the third point is the positive direction of the Y axis. 4.X/Y/Z axis rotation UCS: See the positive direction from the origin to the fixed axis, counterclockwise is negative, clockwise is positive. Rotation means that the two axes rotate to the same angle at the same time to the third axis. 5. Face UCS: Quickly place the X and Y planes on the selected plane. The reference plane can only be a plane, and the surface cannot be placed with UCS. 6. Object UCS: mainly for the X and Y planes, that is, the X, Y axis directions in the X and Y planes are rotated by the object; When the XY plane does not leave the original plane, the direction of the XY axis changes, and one point of the point is the positive direction of the X axis, and the end point closest to this point is the origin. 7. View UCS, regardless of the direction of the three axes of the current UCS X, Y, Z, the view UCS can be placed in the horizontal direction, Y is placed in the vertical direction, so that the mutual view of the different files can be used. Note: In AutoCAD modeling, the important content is the constant switching of the view space and the flexible application of UCS, mainly solid modeling, and the surface modeling function of AutoCAD is weak. The operation of the 3D partial menu: View: (the following view under the view menu) Six plan views: top view, bottom view, left view, right view, main view (aka front view), rear view Four isometric side views: southwest isometric view, southeast isometric view, northeast isometric view, northwest isometric view; all four views are viewed from a 45 degree diagonal. Camera view: Set a view at two points; from the first point to the second point. Entity toolbar: Drawing of three basic systems (cuboid, sphere, cylinder), cone, wedge, ring Stretch modeling: (premise: must be the end-to-end closed body) The default operation is to give a height can also give the stretching angle, the stretching angle is defined: the positive value is getting smaller and smaller, and the negative value is getting bigger and bigger; Stretching along the path: to be perpendicular to the graphic and only to draw on the X, Y surface: chair production, etc. Rotation modeling: There are three parameters to choose from, but they are generally not used. Basic operation: Determine the rotation of one axis with two points. Example: bowl making, round table drawing, etc. Cut: After selecting the object, there are the following tips: Specify the first point on the cut surface according to [Object (O) / Z axis (Z) / View (V) / XY plane (XY) / YZ plane (YZ) / ZX plane (ZX) / Three points (3) ]<Three points> "Object" is an entity that cuts an object (circle, ellipse, arc, two-dimensional spline, or two-dimensional polyline); "Z-axis" is a point on the plane Z-axis (normal) "View" is to specify three points in the view to physically cut the solid; "XY plane" to cut the entity in the XY plane; "YZ plane" to cut the entity in the YZ plane; "ZX plane" to The ZX plane cuts the solid; the "three points" specify three points to define a face to cut the solid (three points form an infinite number of faces on a straight line) Cutting: The same as the cutting operation, except that the cutting does not divide the solid, but forms a plane at the dividing point; it is equivalent to the section, only the section is extracted, instead of actually cutting the object. Interference: It is the calculation of two objects, which is equivalent to the intersection, that is, the original object is not deleted. Coloring toolbar: 2D wireframe: Place a graphic in 2D and display it in a wireframe 3D wireframe: Display a graphic as a wireframe in a 3D view Blanking: hides invisible lines in 3D wireframe graphics Plane coloring: used in the square, the coloring plane is not smooth Body coloring: used more widely, the coloring plane is very smooth Plane coloring with borders: bordered after coloring Coloring with border body: bordered after coloring Entity editing toolbar: Union: Combine two or two fields into one region. Difference: Premise: There must be two or two fields above; the second area is subtracted from the second area by the second area. Intersection: Two or two parts that intersect with the above fields are retained, and the other parts are deleted. Positioning surface: After selecting the tool, select the surface to be stretched, you can transfer the height or stretch along the path; Move face: Move the face; select the face to move and move it; right click twice to exit. Offset surface: Offset of the surface: the positive value is getting larger and larger, the negative value is getting smaller and smaller; the offset of the hole: the negative value increases, and the positive value becomes smaller. Delete face: for rounding: chamfering, punching Rotating surface: rotates the surface by a specified angle on an axis Inclined face: The first point specified is the origin of the tilt axis; the first point is tilted to the second point by a specified angle. Copy face: You can copy a face and the copied face can be stretched. Colored face: The color of a face can be changed to be marked. Copy edge: copy an edge Shading edges: coloring an edge Embossing: Just press a stamp on the body and press Esc twice to exit. After embossing, the area can be operated Clear: The embossed impression can be removed. Segmentation: Two disjoint fixed objects should be separated and available for segmentation. Shelling: The default operation is to turn an entity into a box, which side will delete which side, and which line will delete the two faces associated with this line, open the -ALL-A parameter. Example: Production of tee and tee. Check: Check if the object is a valid 3D solid. Basically no application. Surface operation: Two-dimensional fill: Specify four points. Fill mode: one to three points to connect, two to four points to connect. 3D face: Specify three points to determine a face. You can see the effect after coloring. Example: Drawing of a five-pointed star. 3D Surface: Prompts in the form of a dialog box to draw the following surfaces: Cuboid surface, pyramid surface, wedge surface, upper hemisphere, spherical surface, conical surface, torus surface, lower hemisphere, mesh. Edge operation: hide the intersecting edges of two 3D faces 3D mesh: Determine the points into a single face Surftab1, surftab2: control of 3D mesh parameters, give more than 30, set the smoothness of the rotating surface Pan the surface: the left side of the point path is stretched to the right, and the right side is stretched to the left. Ruled surface: Form a face with two lines or curves. The boundary surface must be four objects to form a boundary surface All options for 3D chamfer are not available. Base surface, L application of the first face chamfer Rounding (the latter parameters are not available) Rounding of three different radii Application of C's application chain: production of ashtray 3D operation: 3D Mirroring: Mirroring with a face as the reference. The default is to use the three points for mirroring. Three-dimensional array: An array of two options (rectangular array, circular array) space. The rectangular array can form a rectangular parallelepiped; the annular array rotates with one axis. Three-dimensional rotation: Two axes are used to determine an axis for rotation. (Example: Making of a chair.) Alignment: One-point alignment, equivalent to alignment movement; two-point alignment: aligns the target object with the reference object at two points, and selects whether to scale the object; three-point alignment: aligns the target object with the reference object by three points. Rendering toolbar: (weaker) can be explained by user-friendly graphics. Rename: Some objects can be renamed. Printing and advanced customization Print: Print in model view, print style sheet new: file - print - new - set in the dialog Basic line width setting in the Printer: laser printer: red line: 0.2; white line to: 0.4 Layout printing: View menu first item: can be set, viewport toolbar application: the first cabinet viewport, the second multilateral viewport, the third item converts the object into a viewport, the fourth view The cut of the mouth; to create a new viewport, you must first delete the contents inside. The layout can also be created; Graphic unit settings: format - unit The reference direction is east Thickness: format - thickness, generally not used; graphic limit: the size of the drawing can be set The function of the button under the status bar: Capture: For the grid, basically not used. Grid: You can set grid points. Useful when capturing and finding. Basically not used Orthogonal: When open, generally only horizontal and vertical lines can be drawn. Polar axis: can set the angle, basically no need Object snap: used to capture special points. It is used more widely. Object tracking: tracking of specific angles Line width setting: It is not a desirable method. Learn to use colors to distinguish graphics. It is not necessary to use line width to distinguish. Import MAX: file_import in MAX, select the file type of dwg. Find and replace: Edit - Find External Reference: Insert - External Reference (large companies use more, suitable for overall control) Use of OLE objects: å…‰æ …å›¾åƒï¼šå›¾åƒçš„调入和修改 autocad安装目录sampledesigncenter:设计ä¸å¿ƒçš„使用 点的过滤,相当于æå–·Xå³è¿‡æ»¤X 备份文件的使用:将扩展å改为.dwg 工具—选项----打开和ä¿å˜----安全选项å¯å¯¹æ–‡ä»¶è¿›è¡ŒåŠ 密ä¿å˜ä¸º2004çš„æ ¼å¼æ‰æœ‰å¯†ç 展开图的绘制:将一个图形展开。 相贯线的绘制:两实体相交时所共有的线段 é€è§†å›¾çš„绘制:平行线的关系——å‘散投影——交与一点,å¯ä»¥ç”»å‡ºé€è§†å›¾ å¿«æ·é”®çš„制作: æ ¼å¼ï¼šå¿«æ·é”®å—æ¯æˆ–æ•°å—或两者组åˆï¼Œ*,英文命令的全称 E.g: 1,*lime:表示输入“1â€å¯ç»˜åˆ¶ç›´çº¿ 2,*circle表示输入“2â€å¯ç»˜åˆ¶åœ† sj,*mline表示sjå¯ä»¥ç»˜åˆ¶å¤šçº¿ 以上内容的输入:工具èœå•â€”—自定义——编辑自定义文件——程åºå‚数,在æ¤æ–‡ä»¶ä¸å¢žåŠ ä»¥ä¸Šæ ¼å¼çš„控制æ“作文本,设置完æˆåŽï¼Œå…³é—AutoCAD,é‡æ–°æ‰“开程åºæ—¶å°±å¯èµ·ä½œç”¨ã€‚ 文件大å°æ–¹é¢:åŒä¸€å›¾å½¢ï¼Œ2004的版本画图å¯æ¯”2002的版本缩å°30% 一些基本尺寸的转æ¢ï¼š 1英寸(1in)=25.4mm 1英尺(1ft)=30.5cm 1ç (1yd)=0.914m 1英里(1mile)=1.61km 1国际海里(1nmile)=1852m æ–‡å—线型的制作 AutoCAD8.0的时候就有这项功能。 线型控制信æ¯ï¼šï¼ˆå¦‚图) å¹»ç¯ç‰‡çš„制作:(如图) èœå•çš„制作:(如图) 浮动工具æ¡çš„制作: 用户定义——用户定义的按钮——进行设置å³å¯ã€‚ å›¾æ ‡çš„åˆ¶ä½œï¼š ä»»æ„工具æ ——å•å‡»å³é”®â€”—自定义——想制作或者想修改æŸå·¥å…·çš„å›¾æ ‡ç›´æŽ¥ç‚¹å‡»ä¸€ä¸‹å³å¯ã€‚ 常用的系统å˜é‡åŠåŠŸèƒ½ 1.pickbox å’Œcursorsize:这二个å˜é‡ç”¨äºŽæŽ§åˆ¶åå—å…‰æ ‡å’Œæ‹¾å–框的尺寸,绘图时å¯ä»¥é€‚当修改其大å°ä»¥é€‚应我们的视觉è¦æ±‚。pickbox 缺çœå€¼ä¸º3,å–值范围为0~32767ï¼›cursorsize 缺çœå€¼ä¸º5,å–值范围为1~100。 2.aperture: 用于控制对象æ•æ‰ï¼ˆObject SNAP)é¶åŒºå¤§å°ï¼Œåœ¨è¿›è¡Œå¯¹è±¡æ•æ‰æ—¶ï¼Œå…¶å–值越大,就越å¯ä»¥åœ¨è¾ƒè¿œçš„ä½ç½®æ•æ‰åˆ°å¯¹è±¡ï¼Œå½“图形线æ¡è¾ƒå¯†æ—¶ï¼Œåº”设置得å°ä¸€äº›ï¼›å之,设置得大一些方便æ“作。缺çœå€¼ä¸º10,å–值范围为1~50。 3.ltscale å’Œceltscaleï¼šå…¨å±€çº¿åž‹æ¯”çŽ‡å› åå’Œå±€éƒ¨çº¿åž‹æ¯”çŽ‡å› å,用于控制éžè¿žç»çº¿åž‹çš„输出比率(å³çŸçº¿çš„é•¿åº¦å’Œç©ºæ ¼çš„é—´è·ï¼‰ï¼Œè¯¥å˜é‡çš„值越大,间è·å°±è¶Šå¤§ã€‚å…¶ä¸ï¼Œltscale对所有的对象有效,celtscaleåªå¯¹æ–°å¯¹è±¡æœ‰æ•ˆã€‚对于æŸä¸€å¯¹è±¡æ¥è¯´ï¼šçº¿åž‹æ¯”率=ltscale*celtscale。这二个å˜é‡çš„缺çœå€¼å‡ä¸º1,å–值为æ£å®žæ•°ã€‚ 4.surftab1 å’Œsurftab2ï¼šç”¨äºŽæŽ§åˆ¶ä¸‰ç»´ç½‘æ ¼é¢çš„ç»ã€çº¬çº¿æ•°é‡ï¼Œè¯¥å€¼è¶Šå¤§ï¼Œå›¾å½¢çš„生æˆçº¿è¶Šå¯†ï¼Œæ˜¾ç¤ºå°±è¶Šç²¾ç¡®ã€‚缺çœå€¼ä¸º6,å–值范围为2~32766。 5.isolines: ä¸‰ç»´å®žä½“æ˜¾ç¤ºåˆ†æ ¼çº¿æŽ§åˆ¶ï¼Œå…¶å€¼è¶Šå¤§ï¼Œåˆ†æ ¼çº¿è¶Šå¤šï¼Œæ˜¾ç¤ºè¶Šç²¾ç¡®ã€‚ç¼ºçœå€¼ä¸º4,å–值范围为0~2047 6.facetres: 用于控制三维实体在消éšã€æ¸²æŸ“时表é¢çš„棱é¢ç”Ÿæˆå¯†åº¦ï¼Œå…¶å€¼è¶Šå¤§ï¼Œç”Ÿæˆçš„图åƒè¶Šå…‰æ»‘。缺çœå€¼ä¸º0.5,å–值范围为0.01~10。 注æ„: isolinesã€facetres的值å–得太大时,图形生æˆã€æ¶ˆéšæˆ–渲染所用的时间就会越长。 系统å˜é‡ä¸ºQTEXTMODE: 类型:整数 ä¿å˜ä½ç½®ï¼šå›¾å½¢ åˆå§‹å€¼ï¼š0 控制文å—如何显示。0ï¼å…³é—“快速文å—â€æ¨¡å¼ï¼›æ˜¾ç¤ºå—符;1ï¼æ‰“开“快速文å—â€æ¨¡å¼ï¼›æ˜¾ç¤ºæ–‡æœ¬å¤–框代替文å—。 2D Desktop Barcode Scanner,Desktop Qr Code Reader,Qr Code Scanner Desktop,Desktop Barcode Reader T97 SUNLUX IOT Technology (Guangdong) INC. , http://www.sunluxbarcodereader.com