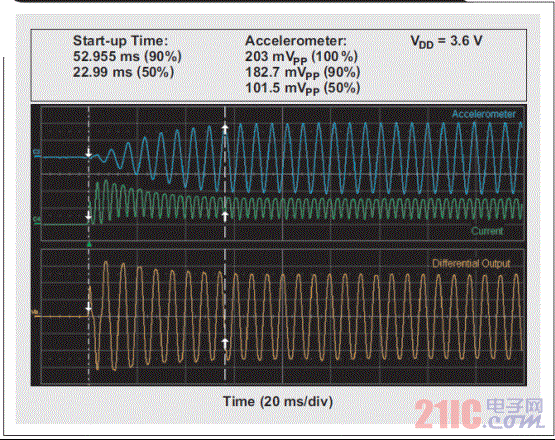
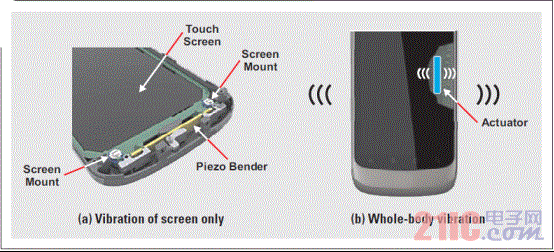
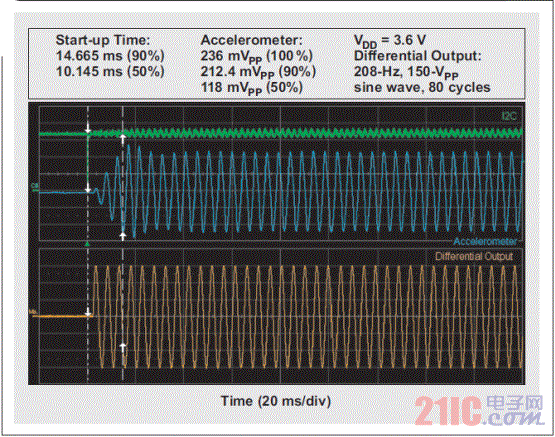
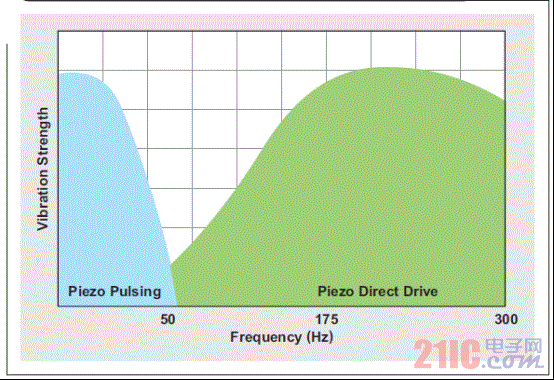
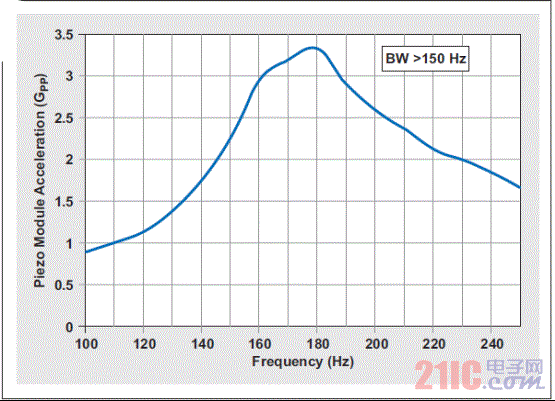
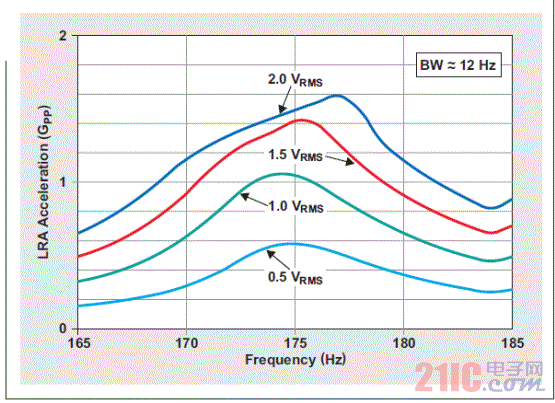
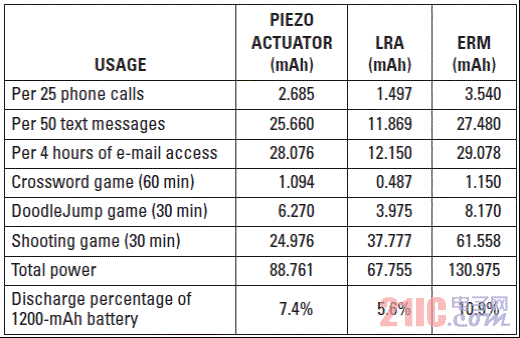
Although most smartphone and tablet users have already experienced haptic technology, the term haptics itself is rarely known to consumers. In terms of its basic definition, "haptics" refers to the science of tactile feedback. The most basic form of application of haptic technology is that the mobile phone prompts the user to call or has a new text message in the inbox. In these cases, the phone uses haptic technology to draw the attention of the user. This article refers to the address: http:// About one-third of smartphones use haptic feedback technology, and the features they implement are more than just vibration alerts. A common example is when users use their mobile phones to write emails or text messages, users experience subtle vibration feedback. When a button is successfully pressed, the phone will vibrate to confirm once. In the case of using haptic feedback, the user rarely has input errors and the operation experience is more satisfactory. Enhance user experience with haptic technology More and more mobile devices, such as mobile phones and tablets, are using touch. The touch interface is so simple and intuitive that the three-year-old will also unlock the smartphone and click on the YouTube icon to view the video playlist. However, touch screens have a serious limitation: because there is no physical or mechanical feedback, user interaction or reminders cannot be achieved. Designing an excellent tactile feedback feature greatly enhances the overall user experience of touch-enabled mobile devices. The application of haptic technology is much more than just user reminders or button confirmation. Standard gesture operations, such as sliding unlocking, finger zooming images, and dragging pages up and down, all have their own tactile/perceptual characteristics. When the user places the picture to the maximum size, the tactile feedback strength also increases. Haptic feedback is also faster when scrolling quickly. If this context-sensitive feedback is combined with audible feedback, the resulting user experience will be highly satisfying and intuitive. In addition, tactile feedback brings another pleasure. Many people use mobile devices to play games. Haptic feedback technology can greatly improve the gaming experience. For example, in a first-person shooter game, the protagonist of the game can truly feel the shock of weapon shooting. Users can feel the collision and bumps of the car in the racing game, feel the elasticity when releasing the slingshot rope in the popular "angry bird" game, feel the guitar strings or piano keys in the playing game, and so on. The imagination of game developers will create unlimited possibilities for experience! Inertial tactile actuator (ERM/LRA) The standard haptic feedback function in the phone is achieved by a small motor called the Eccentric Rotating Mass Actuator (ERM). The motor is driven by voltage to start rotating, and the user can feel the vibration. The haptic feedback driver chip drives the motor in a differential manner so that the motor rotates when a positive voltage is active and stops when the reverse polarity, ie, a negative voltage, acts. This method is very effective when used for vibration reminders. However, when ERM is used in other haptic feedback applications, such as games, etc., the device battery power drops rapidly. ERM has inertia and requires overdrive to rotate faster. The start-up time is the time required for the motor to reach 90% of the rated acceleration, which is typically in the range of 50 to 100 ms. The time range for motor braking or stopping is similar. Triggering a very simple tactile feedback event (eg, a click) takes about 100 to 200 ms. If the application requires repeated haptic feedback events, the delay of the motor type haptic feedback is less than ideal. Another aspect of ERM is the humming sound produced by a rotating motor, which is the noise that can be heard by the human ear. If haptic feedback is combined with audible feedback, this problem can be partially alleviated. However, in a quiet conference room, if someone is texting, everyone can hear the noise. In addition, the ergonomic feedback effect of the ERM becomes inconspicuous due to user operations. The vibration frequency and amplitude are related to a single control voltage. Another type of inertial actuator, the Linear Resonance Actuator (LRA), is used in some smartphones to achieve tactile feedback and vibration alerts. The mechanical structure of LRA is different compared to ERM. It consists of a mass mounted on a spring that vibrates in a linear motion. The LRA must be driven at a narrow resonant frequency. In addition, its startup time is slightly better than ERM. Depending on the manufacturer, the start-up time range is 40 to 60 ms (Figure 1), which is better than the ERM start-up time (50 to 100 ms). By modulating the resonant carrier amplitude, various haptic feedback effects can be produced. Figure 1 Typical startup time for LRA is 40 to 60ms High resolution haptic feedback High-definition (HD) TVs offer higher resolution than standard definition TVs, providing a sharper and clearer picture. Similarly, high-resolution tactile feedback allows the user to experience more pronounced vibrations than the inertial actuator's helium vibration. Piezo or ceramic haptic feedback actuators are used to achieve HD haptic feedback, providing a different experience than ERM/LRA. Piezoelectric actuator When a differential voltage is applied across the piezoelectric actuator, it is bent and deformed to generate vibration. Piezoelectric actuators require high pressure to deform. Depending on the manufacturer, the voltage can range from 50 to 150 VPP. When the voltage is higher, the number of piezoelectric layers is required to be reduced; therefore, when the voltage is 150 VPP, the piezoelectric actuator has about 4 layers, and when the voltage is 50 VPP, there may be 16 to 24 layers. At higher voltages, the piezoelectric actuator has a smaller capacitance due to the reduced number of layers. In other words, the current required to drive the low capacitance haptic feedback actuator is smaller. Piezoelectric actuators are in the form of discs or rectangular strips, also known as benders. The piezoelectric disk is vertically deformed and can be used for Z-axis vibration. The piezoelectric bender can be mounted directly on a “floating†touch screen for screen vibration (Figure 2a). The piezoelectric bender can also be mounted in a small module that can be mounted to the device's housing or PCB to achieve vibration of the entire device (Figure 2b). Piezoelectric modules are popular because of their mechanical integration. Figure 2 Piece shape factor of piezoelectric actuator What makes the piezoelectric actuators have high resolution? The four factors distinguish the piezoelectric actuator from the inertial actuator: 1. Faster start-up: Due to its inherent mechanical properties, the piezoelectric actuator has a very short start-up time – typically less than 15ms, which is 3 to 4 times faster than ERM. Compared to ERM, the overall tactile feedback event duration is reduced by 70ms. This is described in detail in Figure 3. 2. Higher bandwidth: The higher bandwidth of the piezoelectric actuator (see Figure 4) provides a more detailed combination of tactile feedback for more results. 3. Lower noise: Unlike the ERM, the piezoelectric actuator has no mechanical noise generated by the rotating mass. 4. Stronger vibration: Piezoelectric modules can produce higher vibration strength. Figure 5 shows the acceleration characteristics of a commercially available piezoelectric module, while Figure 6 shows the acceleration characteristics of a commercially available LRA. We can see that the piezoelectric actuator produces a peak-to-peak acceleration of 3 GPP compared to the peak-to-peak acceleration of LRA below 1.5 GPP. This higher vibration strength means that piezoelectric modules are ideal for large screen smartphones and tablets. Figure 4 Piezoelectric actuator (ideal module) has a higher bandwidth Figure 6 Acceleration characteristics of the LRA Piezoelectric actuator current consumption Although the piezoelectric actuator requires a higher voltage than the standard inertial actuator, the actual current consumption is lower than the ERM and is the same size as the LRA (see Table 1). Table 1 Power consumption of the tactile feedback actuator in conclusion Compared to inertial actuators, piezoelectric actuators offer significant performance and cost advantages. It has a shorter boot time and helps the keyboard application achieve strong and brisk click confirmation. Its high bandwidth advantage helps achieve a more sensible haptic effect for the user, which is critical for gaming applications. Piezo actuators provide greater vibration and provide tactile feedback for some large consumer devices such as tablets and e-readers. In summary, piezoelectric haptic feedback technology has many compelling features that enhance the tactile feedback experience and help improve the overall user experience of mobile devices. PTFE tapes, also known as thread seal tapes, are commonly used within the plumbing industry as a way to enhance the seal between two pipes. When you think about screwing two pipes together you can see that this will not provide the tightest of seals, especially when water or air tight seals are desired. This is where PTFE tape comes into play, as this type of tape fills in the spaces left behind in the threading in order to create the tightest seal possible. PTFE Fabric With Silicone Adhesive Strong Adhesive Tape,Silicon Tapes,Silicone Fabric,PTFE Fabric With Silicone Adhesive TAIZHOU YAXING PLASTIC INDUSTRY CO., LTD , https://www.yaxingptfe.com