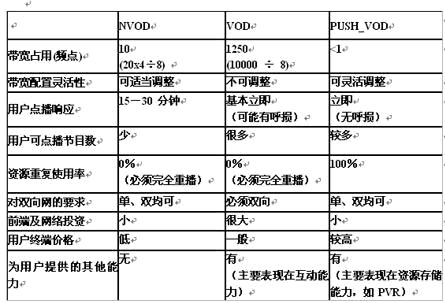
Tags: VOD NVOD PUSH-VOD IPTV This article refers to the address: http:// First, VOD VOD (Video On Demand) video on demand technology is one of the new business hotspots launched on the Internet in recent years (originally produced in Japan, the central computer system directly transmits movies or video programs to families according to the user's on-demand needs) Entertainment systems. Future video on demand is expected to enter other interactive TV services, including games, banking and personal finance, shopping and education services. It is divided into TVOD (True VOD for short VOD) and NVOD (Near VOD). TVOD For each request for on-demand, the server must output a corresponding video stream, which has a very large bandwidth requirement for the network. NVOD can support any multi-user on-demand request. Although the bandwidth problem is solved, each user may have to wait for a long time to get the corresponding service. Three characteristics of TVOD: 1. Based on two-way network 2. Click and put 3. The number of concurrent streams is limited, the number of supported users is limited, and the cost per user is high. Second, NVOD NVOD (Near Video On Demand) is one of the value-added services of the one-way digital TV system. It uses a video server to delay playback of a digital TV program in several digital channels. The user can wait for a period of time to watch the program completely when the program is clicked. Five features of NVOD: 1.NVOD broadcast control system software features: Graphical interface The program layout uses an intuitive graphical interface to distinguish different playback states in different colors. Simple and clear way of operation Support mouse drag and drop selection, support batch add program, add delete simple Automatic allocation of channel resources The system automatically calculates and allocates the number of channels based on program length and program interval. Automatic detection of channel bandwidth Program layout, broadcast separation For database operations. Can realize program layout and broadcast separation Program upload function support Upload the program stream of the local hard disk to the video server Print function support Printable schedules, print preview support During the programming process, the sum of the program bandwidths of all the digital channels of the same frequency point is automatically calculated. If the maximum value is exceeded (38 Mbps at QAM64), a prompt message is given. 2.NVOD program form generation software features: Automatically extract data from the programming database to generate NVOD program forms Encapsulation transmission using MPEG-2 Private section Adopt a single PID structure, can be sent to the multiplexer for multiplexing output The program form is dynamically refreshed as the programming changes The TS stream generation and output are performed in the memory, no file is generated, the loss on the hard disk is reduced, and the TS stream generation speed is increased. The program form data contains the real-time clock information of the front-end server for synchronizing the set-top box clock with the front-end clock. 3.NVOD (Near VOD) transmission network: based on broadcast network 4.NVOD advantages: no user limit, low unit cost 5. NVOD disadvantages: long waiting time (10-15 minutes) Third, PUSH-VOD Introduction to PUSH-VOD PUSH-VOD is a video push service. This system allows TV programs or popular science e-books to be directly transmitted to each set-top box via satellite and stored in it; so that ordinary people can see these programs and read e-books on-demand. The core idea of ​​the PUSH-VOD system PUSH-VOD is a broadcast pre-push service using a small amount of resources. In the off-peak hours, the hot resources that the user cares about are pushed, and a large amount of things can be stored between the user-side set-top boxes, which can also bring certain interactive benefits. The concept of PUSH-VOD is not conceived out of thin air. Instead, it is modeled after a very similar concept. In the Internet business, there are pre-pushing businesses in Europe and the United States. Internet services and cable TV on-demand services also have a large amount of access in a short period of time, which has caused a great buffer and can not be connected. The EU countries have pre-pushed, and everyone interested in this business can order in advance, pre-download and watch. In the past, VOD was different, and some resources were used to push at a fixed time and large capacity. Application of PUSH-VOD system in several environments 1. Application of PUSH_VOD system in one-way cable television network The one-way network can give full play to its advantages, because the idea and launch of the PUSH-VOD is to enable operators to obtain interactive functions without the need for large-scale investment and without the need for two-way network transformation to obtain value-added services. The proceeds. PUSH-VOD makes it play its advantages well in a one-way network. The same is true for users. You can order your favorite videos, audio, pictures and other content at any time. It is also possible to perform functions such as fast forward, fast rewind, search, and repeat play, and the initial investment for operators is very small. 2. Application of PUSH-VOD system in two-way cable television network If the program of the hot spot can be pushed into the internal hard disk of the set top box, the dedicated channel and the broadcast stream resource actually occupied by the user when on demanding are greatly reduced, and the effect of the system operation can be effectively improved. 3. The application of the PUSH-VOD system in a dedicated environment. At present, there are some special systems like the party member education system and the rural information platform. They all have some common characteristics. The network environment does not necessarily have the conditions for two-way interaction, especially in remote areas, it is impossible to carry out large-scale two-way transformation. The content delivered has a lot of information, and it is likely to be video, a lot of text, and a lot of pictures. Users must have full initiative when viewing, watching what, and how to watch. 4. Application of PUSH-VOD system in IPTV The true two-way system or the real IPTV system PUSH-VOD is really useful, which is similar to the two-way network, and is also designed to solve the extreme situation of end user bandwidth shortage. However, the PUSH-VOD in the IPTV environment is slightly different from the PUSH-VOD in the wired network, and the amount of data is pushed to the user's terminal by using the free bandwidth of the service network. In the wired system, a dedicated channel is used for large-scale data volume push, and some movies may take 8 hours to download, but the PUSH-VOD system is only pushed down in 10 minutes. Fourth, VOD operators have encountered those problems Nowadays, the VOD service operators that have been implemented have encountered some problems. During the peak hours, there are not enough resources. During the peak hours, many users will focus on one or two hot movies, resulting in a large concentration of resources in a short period of time. Within the one-way network, we can't provide VOD services at all, and we need to carry out two-way transformation. How do current operators solve these problems? The problem of insufficient resources during peak hours is now impossible to increase the number of flows and increase the number of IPQAMs. On this basis, the operator has moved forward the media server and adopted a multi-mirror server. Based on this, we have made in-depth thinking about whether we can further translate the server and further spread the resources. At this time we think of the resources of the vast number of end users, whether we can use the resources of the end users to achieve our VOD business. We found that when we actually pushed the VOD service to the user's set-top box, IPQAM also increased. This is the idea of ​​PUSH-VOD. The core idea is to download a large amount of content to all users' local terminals simultaneously in a broadcast mode in a centralized period, so that the system only needs to perform local operation of the terminal when the user actually uses it. Network resources provide personalized service. V. Comparison of three VOD systems Compare the types of cable digital TV service services that are currently common. One is the most basic broadcast TV service, one is NVOD, and the other is true VOD service. What are the differences between these types of services: the broadcast-type business is still like the previous TV. Although there are more stations, the general audience has no choice, no choice of content, and what to look at. NVOD has a certain degree of selectivity. We can choose to view the content at different time periods. The choice of content is fixed or determined by the operator. The interactive TV VOD service has very good interactive capabilities, emphasizing the ability to interact, and there are many optional services. It is clear that the interactive TV business is a very popular business. However, it has not been promoted in large quantities. It is only better in big cities. Many areas are in translation, which involves the problem of interactive TV. The front end needs to invest a lot of manpower, financial resources and material resources. NVOD can be done with a small number of servers and a small amount of resources, but to achieve interaction must be a two-way transformation. From the point of view of the increased investment required to realize the service, broadcast TV has been done, NVOD is very small, and there are many interactive TV services. It can be seen that the interactive TV service is in contradiction with the PUSH-VOD system. Although the resources are very expensive, they have very good advantages and good interactivity. Let's take a look at the comparison of PUSH-VOD and other VODs to see what are the advantages and disadvantages. First make a hypothesis, on-demand in 500,000 cities. If there are 10,000 users who need on-demand services, our TV station broadcasts 20 sets of popular programs every day, and each station broadcasts 8 programs, and each program is averaged at NVOD. 4 sections to play. In comparison, the frequency resource that needs to be occupied for NVOD is 8 frequency points, and PUSH-VOD needs to occupy 10 frequency points. For VOD, there is no such concept of algorithm, how many users need to concentrate the bandwidth and frequency. For PUSH-VOD, most users download the hard disk, using local resources instead of bandwidth resources. Capacitor Motor,Furnace Capacitor,Start Capacitor,Capacitor Start Motor Wentelon Micro-Motor Co.,Ltd. , https://www.wentelon.com