data collection Definition: Use a variety of lightweight databases to receive data sent from the client, and users can use these databases to perform simple queries and processing tasks. Features and challenges: High concurrency coefficient. Products used: MySQL, Oracle, Hbase, Redis, MongoDB, etc., and the characteristics of these products are different. Statistical Analysis Definition: Quickly import massive amounts of data from the front-end into a centralized large-scale distributed database or distributed storage cluster, and use distributed technology to perform ordinary queries and classifications of the centralized massive data stored in it, to This satisfies most common analysis needs. Features and challenges: The amount of imported data is large, the amount of data involved in the query is large, and the query request is large. Products used: InfoBright, Hadoop (Pig and Hive), YunTable, SAP Hana and OracleExadata. In addition to Hadoop which is mainly used for offline analysis, other products can be used for real-time analysis. Mining data Definition: Perform data mining based on the previous query data to meet high-level data analysis needs. Features and challenges: The algorithm is complex, and the amount of data and calculation involved in the calculation are large. Products used: R, Hadoop Mahout. From the perspective of corporate decision-making, in any industry, in any field, it is still the human brain that promotes dataization or big data calculations to improve corporate decision-making and corporate strategy implementation. The only difference is that the leadership that used to rely on rich corporate experience and information integration capabilities to make decisions now relies on high-performance parallel computer processing technology to process massive data sets, and distributed calculations to make final strategic decisions. Using such technology can greatly improve the accuracy and efficiency of leadership decision-making. In fact, the role of big data is not only to provide help for various decisions, it can even use massive data to shape individuals, user analysis will no longer be applicable, because big data can even shape users. The law of large numbers tells us that if the experiment is repeated many times, the frequency of random events is similar to its probability. "Regular random events" often show almost inevitable statistical characteristics under the condition of a large number of recurring occurrences. The data itself does not produce value. How to analyze and use big data to help the business is the key. With the increasing power of the computer's processing power, the greater the amount of data you can obtain, the more value you can unearth. If banks can understand risks in a timely manner, our economy will be stronger. If the hospital can detect the disease earlier, our body will be healthier. If telecommunications companies can reduce costs, our phone bills will be cheaper. If the traffic dynamics and weather can be mastered, our travel will be more convenient. If shopping malls can dynamically adjust their inventory, our products will be more affordable. From a commercial point of view, mining and analyzing users’ behavior habits and preferences from the huge and complex data, developing products and services that are more in line with user preferences, and tailoring and optimizing products based on user needs to optimize user experience , The ultimate commercial benefit is the value of big data in the commercial society. Regardless of business, using big data to predict possible disasters, using big data to analyze possible causes of cancer and find out treatments are all undertakings that can benefit mankind in the future. Ultimately, we will all benefit from big data analysis. In the era of big data, people who no longer rely on sampling can obtain and analyze more data, and more clearly discover the details that samples cannot reveal. With the increasing power of computer processing, artificial intelligence machine learning systems continue to upgrade, The value of huge data to people has risen exponentially. Repeated experiments and the accumulation of big data have allowed humans to discover various laws and predict the future.
Antenk PLCC connectors Series Sockets are low profile, thin wall sockets designed to convert plastic leaded chips to a thru-hole PCB format on a .100" centerline grid.Antenk's superior precision stamped contact design provides consistent, high retention contacts for all size chips.
PLCC Connectors -PLCCSockets Plcc Socket,Plcc Connector,Plcc Socket Connector,Smd Plcc Connector,PLCC Connector DIP,PLCC Connector SMT ShenZhen Antenk Electronics Co,Ltd , https://www.antenkelec.com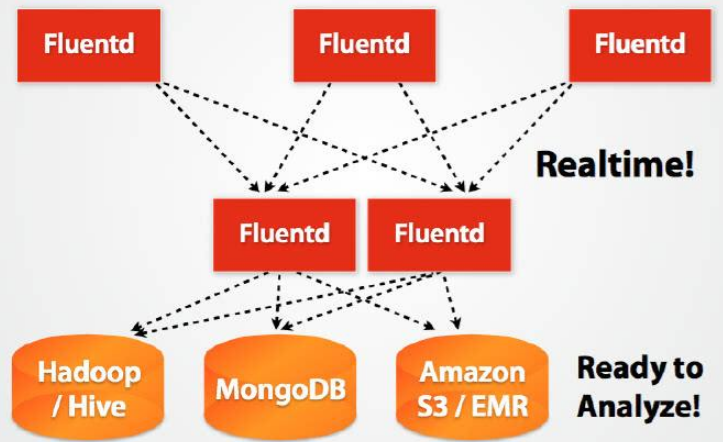

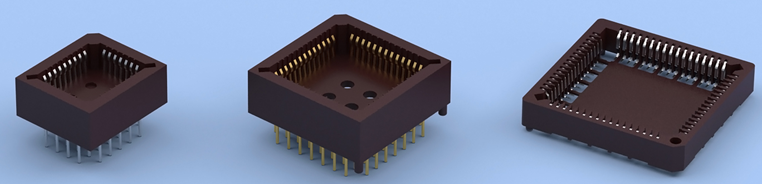
A PLCC socket is a component that connects a chip carrier to an electronic circuit via surface-mounting or through-hole technology.
Plastic leaded chip carriers (PLCCs) are used in surface-mount technology where electronic circuits are produced, and components need to be mounted or placed directly onto a printed circuit board (PCB). The chip carrier is placed in a PLCC socket, which is either surface-mounted or features through-hole technology. A specialised tool called a PLCC extractor is needed to remove the chip carrier from the PLCC socket.
What are PLCC sockets used for?
PLCC sockets are used in surface-mount device (SMD) and surface-mount technology (SMT) applications. PLCC sockets made of heavy gauge copper alloy are compatible in high shock / high vibration applications. PLCC sockets made of rolled-leaf copper are useful in low-cost computer applications.
Types of PLCC sockets
The two primary categories of PLCC sockets are:
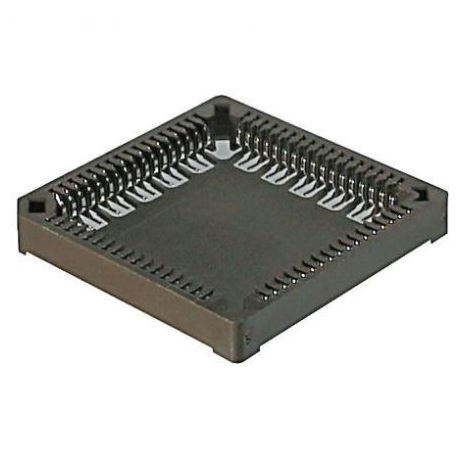
Surface-mount PLCC sockets, which are used in devices sensitive to heat from the reflow process. These allow for component replacement without redesigning or reworking the entire PCB.

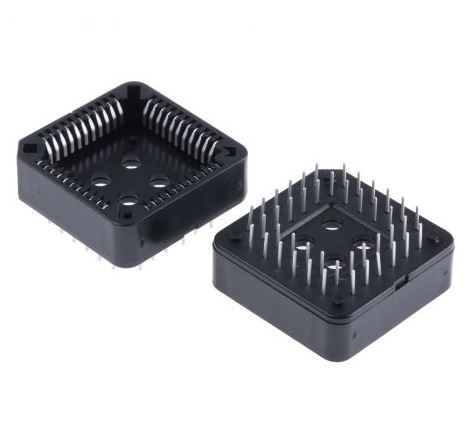
Through-hole technology PLCC sockets are necessary when a device requires stand-alone programming with flash drives or memory devices. These are also beneficial for prototyping activities where wire wrapping is required.

The three major processes of big data processing and the value of big data
Three major processes of big data processing