ZigBee SoC with positioning Today's wireless RF transceivers, microcontrollers, and system-on-a-chip (SoC) semiconductor devices compatible with IEEE 802.15.4 for ZigBee are quite popular. The highly integrated, versatile SoC solution is an important factor in enabling ZigBee wireless networks to be used in a wide range of applications, including industrial surveillance, home and building automation, sensor networks, and even wireless medical solutions. Adding the positioning capabilities of radio frequency devices to the above solutions has greatly increased the value of these networks. GPS Positioning data can significantly increase the value of the information exchanged in many applications. For patient monitoring, asset tracking, inventory control, security, warehousing, manufacturing logistics, and related applications for highly sensitive services and billing, location capabilities can be said to drive the development of wireless sensor networks. Node or sensor location information also facilitates the delivery and adjustment of the wireless network. For example, a wireless node may obtain location information using an existing system such as the Global Positioning System (GPS). However, GPS-type systems can be quite expensive and can be too power hungry and complicated for low cost and wide range of simple network applications. In addition, GPS can effectively and accurately perform positioning functions in an outdoor environment, but this is not necessarily the case indoors. In many wireless personal area network (WPAN) applications, the attractiveness of a network with positioning capabilities is low-cost sensor devices and automatic operation at low power for long device life. Due to the diversity of ZigBee sensor networks and the expected popularity in the future, regional positioning is likely to be one of the most exciting features of this type of wireless system. The idea is to add positioning capabilities to a large number of ZigBee networks in a simple and cost-effective way, adding positioning capabilities to the sensor node silicon device, which only adds a little bit of complexity and cost. If such location modules are integrated into the chip and the location is estimated using existing signal indicators during wireless signal processing, such as Received Signal Strength Pointer (RSSI), the increased size and power consumption and position estimation can be performed. The complexity is kept to a minimum. Radio frequency positioning is a rather complicated process. Through the distributed method (algorithm), the whole process can be divided into multiple manageable work items, which not only can reduce the amount of resources required by the node, but also can significantly reduce the position-related compared with the centralized method. Network traffic. ZigBee SoC with built-in positioning engine For most ZigBee-type wireless applications, to minimize the cost and design complexity of the application system without compromising the functionality of IEEE 802.15.4/Zigbee technology, a system-on-a-chip device with optimal design is critical. A true system-on-a-chip solution that combines all the operational functions of a wireless RF transceiver, data processing unit, memory, and user application functions into a single silicon chip to achieve high performance, low cost, and fast time to market. advantage. The reason why low power consumption can be used is because the built-in special functions of the chip are closely interacted, which greatly reduces the resources consumed. With minimal system bill of materials (BOM), smaller size and fewer components, easier assembly and testing, and simple and reliable design, manufacturing costs are reduced and time-to-market is accelerated. Figure 1 shows a representative CC2431 in a commercially available silicon chip solution. This is a true system-on-a-chip CMOS device that not only performs high-performance but also satisfies IEEE 802.15.4/ZigBee operating in the 2.4 GHz ISM band. The wireless standard requires low cost and low power consumption. The IEEE 802.15.4 standard 2.4 GHz PHY has considerable potential because the 2.4 GHz ISM band has the widest bandwidth and is globally versatile, enabling the development of the global market and the flexibility of application design. The CC2431 combines the high-performance 2.4GHz Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) radio frequency transceiver with the industry-proven compact high-efficiency 8051 microcontroller, 8KB RAM, 128KB embedded flash, and other useful support features. One of these is the powerful RSSI positioning engine for low-power ZigBee wireless sensor network applications such as asset tracking, patient monitoring, inventory control, security and pilot networks. One of the main functions of the on-chip positioning engine is the distribution algorithm, for example, position calculation at each node. Since only the calculated position is transmitted in the process, rather than the data used for the calculation, the position calculation at the node can reduce the network traffic and communication delay that occurs in the centralized algorithm. Figure 1 ZigBee SoC device with positioning function Distributed Localization (Distributed LocalizaTIon) The CC2431's positioning engine is a digital hardware block that enables wireless nodes to determine their own plane position coordinates in a fast and efficient manner in IEEE 802.15.4 or ZigBee networks. By using the signal values ​​received by multiple reference nodes or other dynamic neighboring nodes of the same engine, the most probable location can be calculated, calculated, and estimated to complete the positioning of the wireless node. The positioning engine module is designed to be easy to use and interface with the on-chip microcontroller. This stand-alone module consumes a lot of power and is fast, so it can be used continuously without consuming the computing resources of the device. In a network, a node with a known location is called a reference node, and a node whose location is unknown and needs to be calculated is called a blind node. Based on the information received by the nearest reference node, the CC2431 can use the distributed positioning function to know the location of the node to be tested. The network traffic is limited to the nodes covered by the (to be tested) node's communication range, and does not extend to the central nodes that may be far apart. This distributed method can handle a large number of nodes to be tested on the same network, and the network traffic of the centralized method will increase sharply due to too many nodes to be tested. The necessary information exchanged between the reference node and the node to be tested is the X and Y coordinates of the reference node. The information received by the reference node contains the measured RSSI value, and the positioning engine calculates its own (X, Y) coordinates based on the reference (X, Y) coordinates and the RSSI value. The RSSI value between the two radios is deeply affected by the environment (change). To compensate for this change, the CC2431's positioning engine collects data from 3 to 16 reference nodes for calculating the position. If the received data comes from more than 16 nodes, the received reference node locations are sorted and the 16 strongest reference RSSI values ​​are used. The actual indoor measurements made by the ZigBee network using the CC2431 are shown in Figure 2. Figure 2 Distributed positioning of CC2431 in conclusion In addition to the considerable business opportunities, the application of low-power wireless networks can improve the safety, comfort and efficiency of daily life. ZigBee with high stability IEEE 802.15.4 standard has technical quality and industry support to promote the popularity of wireless sensor solutions. The positioning engine integrated in CC2431 can use the existing ZigBee infrastructure to perform positioning functions, and can perform distributed position estimation based on the 'indoor intelligence' accuracy of sensor nodes in ZigBee network, which is not only energy-saving, but also can greatly reduce the communication station. The funds required. Important location information can be used for location-sensitive services, tracking and monitoring, and navigation purposes.
Application-Specific Integrated Circuit refers to an integrated circuit specifically designed to perform a specific computing task. It is very common to use ASIC for mining in the field of blockchain. This article will analyze the principle of ASIC mining and why it should be anti-ASIC.
For Bitcoin, mining has gone through four stages: CPU, GPU, FPGA and ASIC. GPU is naturally suitable for parallel simple operations, so the execution of SHA256 is much higher than the CPU. FPGA is a programmable hardware, because it has a certain degree of universality, so the unit price will be relatively expensive. ASIC has a large initial design investment, but the unit price will be cheaper after mass production. Therefore, if you can determine that the market size is relatively large, the use of ASIC technology will be the most cost-effective.
In a nutshell, mining is running complicated calculations in the search for a specific number. Whether it`s an ASIC miner or a GPU mining rig, mining hardware must run through many calculations before finding that number. In proof of work systems like Bitcoin, the first one to find that number gets a reward - at the time of writing, 12.5 Bitcoins worth around $96,850. That reward will fall to 6.25 Bitcoins in May 2020. Antin S19J Pro 96Th,Antin S19J Pro,S19J Pro 96T Antminer,s19j pro antminer,s19 xp antminer Shenzhen YLHM Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.ylhm-tech.com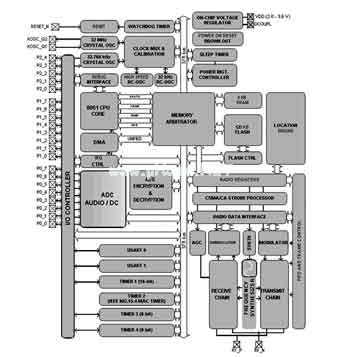
This is the basic principle of ASIC.
There are so many people and powerful computing systems trying to mine Bitcoin that miner groups form to find that number and share the profit. Even more, the faster your hardware, the more you earn. That`s why people who can afford it opt for ASIC miners because it gives them the greatest chance of earning cryptocurrency in exchange for their investment.
Each cryptocurrency has its own cryptographic hash algorithm, and ASIC miners are designed to mine using that specific algorithm. Bitcoin ASIC miners are actually designed to calculate the SHA-256 hash algorithm. In the case of Litecoin, it uses Scrypt. That means technically they could mine any other coin that`s based on the same algorithm, though typically, people who buy ASIC hardware designed for Bitcoin mine that specific digital currency.