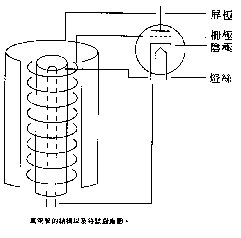
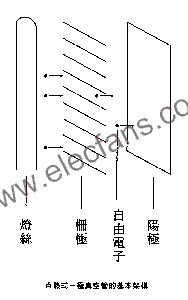
The invention of the electron tube is as dramatic as the discovery of penicillin and tires: in the laboratory, several unwashed experiment dishes near the window, some molds accidentally floated out of the window, and the scientists were surprised to find that some fell into the experiment dish. The mold in the can inhibit the spread and growth of bad bacteria. After being analyzed experimentally, the mold has become one of the effective and widely used antibiotics; the same scenario also happened in the experiment of studying rubber, accidentally breaking the glass. The sulfur in it is poured into the melted rubber liquid, and the rubber becomes a hard and tough material after solidification. Of course, the tube is not for no reason to experiment with several metal plates encapsulated in a vacuum glass bottle. It has a story with Edison, the inventor. Before that, I would like to ask a small question: Is the direction of "current" in circuit analysis the same as the direction of "electron" flow? The answer is no, the direction of current and electron flow is exactly opposite. Scientists in the past could not observe the direction of electron flow, so it was uniformly stated that a certain pole of the battery was set as the positive pole, and its voltage was a positive voltage, and the current flowed from the positive pole to the negative pole to form a closed loop. Due to the unified statement and practice of everyone, there has been no conflict for many years. Until modern scientists have more sophisticated equipment, after observation, they overturned the previous statement: "It turns out that the electrons flowed from the negative end of the battery. "! (In other words, electrons flow out from the negative end of the horn of the amplifier and return from the positive end of the horn) As a user, you don't need to care about what is true, just follow the scientist's conclusion. This paragraph is because after Edison invented the light bulb, he found that the filament of the light bulb he produced always burned out from the positive extreme, so he further experimented by adding a small metal plate to the bulb, and after lighting, the metal plate was connected to the meter and applied a positive voltage respectively. As well as negative voltage, observe the current situation. For the science at that time, it was impossible to generate current no matter how connected the metal plate was in a vacuum state, but when something strange happened, Edison found that a substance (in fact, electron) would pass through the metal plate and would From the negative electrode of the battery to "jump" to the positive electrode, this discovery certainly aroused greater experimental motivation. This phenomenon is called the "Edison effect." This is also the first time scientists have questioned the direction of current flow and the phenomenon of free electrons flowing in space. The reason why metals can conduct electricity is because metals have more free electrons, which facilitates the mutual flow of electrons. Therefore, electronic materials must be made of materials with good conductivity. There is also a characteristic of electrons. Electrons with negative charges are easily attracted by positive voltages, so-called repulsion of the same sex and attraction of the opposite sex. It is also known from the Edison effect that when heating a metal substance, the free electrons active in the periphery of the proton are prone to dissociation, and the high temperature leads to enhanced electron activity. At this time, if there is a strong positive voltage in the space, the free electrons will be in Flowing in space. Based on the knowledge that was already known at that time, J.A. Fleming manufactured the first diode tube in 1904, and De Forest Lee improved the diode and manufactured it in 1907. The first triode, since the successful development of the diode, the application of the electron tube began to realize, and the development of the electron tube has been very fast since then. (See Figure 1 for details) The triode is the most basic electron tube The electronic tube is also called "Vacuum Tube", which means that the inside of the glass bottle is evacuated to facilitate the flow of free electrons and can also effectively reduce the oxidation loss of the filament. Diodes, triodes, and pentodes literally represent the number of basic "poles" inside the tube. The tube has three most basic poles. The first is the "cathode" (represented by K): the cathode is of course negative. It is the place where the electron flow is released. It can be a metal plate or the filament itself. When the filament heats the metal plate, the electrons will come out and be scattered in a small vacuum glass bottle. The second pole is the "Plate" (represented by P). Basically, it is the outermost metal plate of the tube. When you see the darkest gray or black metal plate on the outermost layer of the tube, it is usually the screen. The screen electrode is connected to a positive voltage, which is responsible for attracting the electrons emitted from the cathode (using the principle of heterosexual attraction) as the end point of free travel of electrons. The third extremely "gate" (Gird, represented by G), from the structure, it is like a thin coil of coils, just like a fence, fixed between the cathode and the screen, the electron flow must pass through the grid To the screen electrode, passing a voltage between the grids can control the flow of electrons. Its function is like a faucet, with the function of circulation and blocking. The engine must have fuel to operate, and the working power of the electron tube is electric energy. Among the electrodes of the electron tube, the most important one should be the cathode, which is responsible for releasing electrons as the basis of all work. The earliest electron tube used the filament directly as a cathode because of its simple construction principle. In other words, when the filament was lit, as the temperature of the filament increased, electrons were released from the filament and went straight to the screen electrode through the grid. This kind of tube is called "direct heating tube". 300B belongs to this type of electron tube. Compared with other modern five-pole electron tubes, 300B has a simple structure and low output power. The filament (Filament) can be made of different materials. Since the direct-heating triode directly uses the filament as the cathode, the characteristics of the filament directly affect the performance of the direct-heating tube. Basically, the filament of the electron tube can be divided into three kinds of materials. The first one is of course high temperature resistant tungsten. The high-purity tungsten wire is drawn into a thin wire, wound around the innermost layer of the electron tube, and the temperature can be increased after being energized. But the tungsten wire must be heated to more than two thousand degrees before the electrons can dissipate. Therefore, when the tube made of tungsten wire is lit, it will emit a dazzling brightness and the temperature is scary. Don't be surprised, it's not that the tube is about to burn out, but that it is! However, lighting the tungsten wire consumes a lot of power. The advantage is that the tungsten wire is very durable, and it is generally used in larger power or long-life electronic tubes. In some cases, the life of this vacuum tube can reach tens of thousands of hours. It can be used as a light bulb in the home. It is durable and decorative, and can be counted in one fell swoop! The other filament uses thorium-tungsten alloy, it only needs to heat the filament to more than one thousand degrees to work, which is more power-saving. The most commonly used is the oxidized alkaline earth filament. It is coated with a thick layer of oxidized alkaline earth on the outside of the filament, which looks close to a white-gray substance. It only needs to be heated to about 70 degrees (it looks (Approximately dark red), you can get a sufficient amount of electrons, so the working temperature is the lowest and the most power saving. Generally speaking, only need to supply DC of about 6.3V, it can work normally. Of course, the direct-heating tube has its inherent advantages, but it has a fatal disadvantage, that is, the cathode is easy to change its characteristics due to the temperature change of the filament. When the filament voltage fluctuates, or when the filament is supplied with alternating current, the cathode is in an unstable state. Therefore, some people advocate that direct-heated electronic tubes should be powered by DC, and others emphasize that they must be powered by AC to avoid damage to the cathode. This kind of debate has long been a topic of debate in the audio industry. The stability of the side heating tube is high In this way, the electron tube seems to be much more stable. Because the volume and heat storage of the metal sleeve are higher than that of the traditional filament, even if the filament temperature changes temporarily, or even temporarily stops heating for a few seconds, the temperature change of the metal plate is limited. That is the main reason why some electronic tubes can still sing for more than ten seconds after being turned off. Since the cathode and the filament are independent, the cathode plate must be heated indirectly by the filament, so the filament is changed to tungsten filament again for durability, and a layer of white magnet is coated on the outer layer of the tungsten filament, which is insulated on the one hand, and also has a stereotype effect. Due to the poor indirect heating effect, the cathode metal plate will be coated with thorium, barium or other substances conducive to electron emission. Therefore, the metal plate of the electron tube always looks gray and black, unlike the normal metal plate, and because it must rely on the hand when making and assembling, there will always be many small scratches on the metal plate. When users buy the electron tube Don't worry about it accidentally. What is the difference in the use of direct-heating tube and side-heating tube? For the general user, it is not necessary to care about the difference between the direct heating tube and the side heating tube, but for the designer, due to the indirect heating of the side heating tube, the filament current is usually large, and the structure of the side heating type The cathode metal plate must be heated, so there is a slow heating period after booting. If it is the front stage, a delay design must be done to prevent the start pulse from hurting the back stage. According to the development process, the earliest electron tube is of course a direct-heated design. The diode was first developed. The function of the diode is just like the current two-pole transistor, which has the function of rectification and internal detection of the radio. The diode is properly designed. , Can also become a regulator. Since the working principle of the electron tube is very simple, many scientists joined the research and development after the first electron tube was successfully manufactured. The first triode was successfully manufactured by an American scientist in l907. Since then, the advent of the radio era has begun, saying goodbye to the phonograph and entering the era of amplifiers. How the tube works After disassembling an electron tube, it is drawn in the drawing. It can be seen from the figure that when the filament is lit, the temperature of the filament gradually increases. Although it is in a vacuum state, the temperature of the filament is transferred to the cathode metal plate by radiant heat. When the temperature of the cathode metal plate reaches the temperature at which electrons are free, electrons will fly out of the metal plate. At this time, when the electrons are negatively charged and a positive voltage is applied to the screen, the electrons will be attracted and fly toward the screen metal plate, passing through the grid to form an electron flow. The grid is like a switch. When the grid is not charged, the electron flow will steadily pass through the grid to the screen. When a positive voltage is added to the grid, it is attractive to the electrons and can enhance the speed and power of the electron flow; Conversely, when a negative voltage is added to the grid, the principle of same-repulsion electrons must bypass to reach the screen. If the grid has a large structure, the electron flow may be completely blocked. The grid can be used to easily control the flow of electrons, connect the input signal to the grid, add an appropriate bias voltage, and put a resistor on the screen string to achieve the purpose of signal amplification. The tube is also like the transistor, with a variety of amplification forms (in fact, the amplification form of the transistor is an application extending from the tube), combining different electronic materials such as resistance, inductance, transformers and capacitors, etc., can create ever-changing electronic product. Looking at the inside of the tube wall, you can see a mercury-like film adhered to the glass wall, which is a design that extends the life of the tube. Except for a few low-pressure electron tubes (not referring to low working voltage, but the existence of low-pressure gas inside the electron tubes), most electron tubes must be evacuated to work properly. The pins of the tube are metal pins. Although they are encapsulated in glass, there is still a chance of air leakage between the glass and metal pins. The metal vapor deposited in the glass tube (that is, getter) will interact with the gas. Its purpose is to absorb the gas to maintain the vacuum inside the tube. After this thin layer of metal is oxidized, it will turn white, indicating that the tube has already leaked, so if you break the tube, this layer of evaporated material will also turn white, so when buying an old tube, you should also Pay attention to the condition of the vapor deposits. Mercury is better. If it starts to pale and peels off, it means that the tube has entered old age.
The standard orifice plate flowmeter has the characteristics of simple structure, easy maintenance, stable performance and reliable use, etc.
To measure the flow of gas, steam, liquid and natural gas, widely used in petroleum, chemical, metallurgy, electricity, heating, water supply and other fields of process control and measurement.
Standard Orifice Plate,Orifice Plate,Annular Orifice Plate,Orifice Plate Flow Meter Kaifeng Chuangxin Measurement & Control Instrument Co., Ltd. , https://www.kfcxflowmeter.com
The direction of current and electron flow happens to be opposite 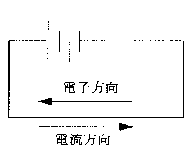
In order to solve the problem of the filament of the direct heating tube, the tube designer decided to separate the filament from the cathode. Put a metal sleeve on the side of the filament to let the filament heat the metal plate directly. The electrons are emitted from the metal plate. This kind of heating method is called "side heating tube". 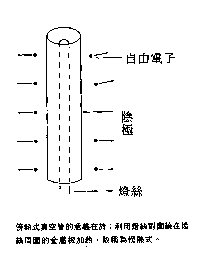
Now, let's take a closer look at the working principle of the simplest tube.