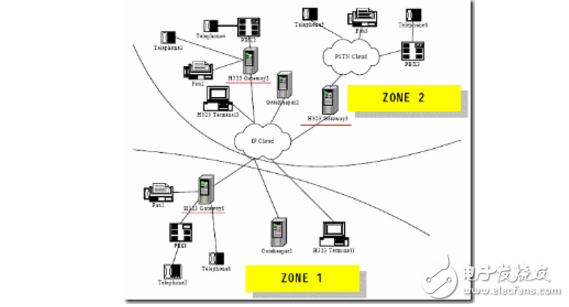
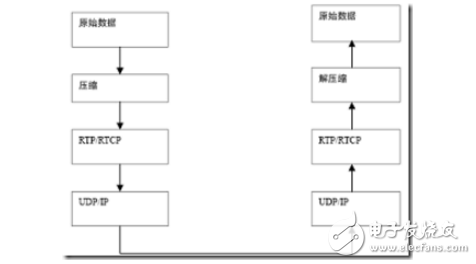
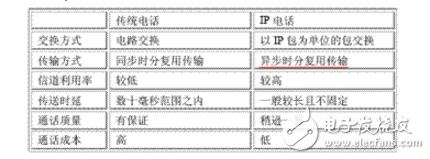
The basic principle of VoIP is to compress the voice data encoding by the voice compression algorithm, and then package the voice data according to the TCP/IP standard, send the data packet to the receiving place through the IP network, and then string the voice data packets. After decompression processing, the original voice signal is restored, thereby achieving the purpose of transmitting voice by the Internet. The core and key device of an IP phone is an IP gateway that maps the regional telephone area codes to the corresponding regional gateway IP addresses. The information is stored in a database, and the data connection processing software will complete functions such as call processing, digital voice packaging, and route management. When the user dials a long distance call, the gateway determines the IP address of the corresponding gateway according to the telephone area code database data, and adds the IP address to the IP data packet, and selects the best route to reduce the transmission delay, and the IP data packet arrives through the Internet. The gateway to the destination. In some areas where the Internet has not been extended or temporarily not set up, routing can be set up, and the nearest gateway can be transferred through the long-distance telephone network to realize communication services. VoIP is a technology that focuses on IP telephony and introduces corresponding value-added services. Internet telephony: A voice call method based on Internet transmission. It is usually a call between a PC and a PC. IP telephony interconnected with the public telephone network: Voice transmission over broadband or dedicated IP networks. The terminal can be a PC or a dedicated IP phone. Traditional telecom operators' VoIP services: transmit voice over the backbone IP network of the telecom carrier. The services provided are still traditional telephone services, using traditional telephone terminals. By using an IP calling card, or by prefixing the dialed telephone number with an IP dialing prefix, this uses the VoIP service provided by the telecommunications carrier. VoIP is relatively cheap. This is because VoIP phones are just one application on the Internet. In essence, VoIP phones are no different from e-mail, instant messaging or web pages, and they can all be transferred between machines connected via the Internet. These machines can be computers, or wireless devices such as cell phones or handheld devices. The traditional telephone and fax services are generally implemented by accessing the PSTN provided by the telecommunications bureau. This type of access method uses a circuit switching method that monopolizes the communication line. When using long-distance services, the cost is high, as shown in Figure 2. Figure 2 Schematic diagram of a traditional telephone network Our VoIP application uses IP networks to replace some of the PSTN network functions for voice data transmission, using packet switching technology. The VoIP network built on the H.232 protocol group is shown in Figure 3 below. In this architecture, the overall block diagram is shown in the figure. Shown. As can be seen from Figure 2, the components of the H.323 system in the access network are called H.323 entities (enTIy), which include H.232 terminals, gateways, gatekeepers, multipoint controllers (MC), multipoint processing. (MP) and Multipoint Control Unit (MCU Muhipoint Control Unit). Regarding the specific meaning of these entities, the content of this section will be analyzed in Section 7. Figure 3 Schematic diagram of VoIP network based on H.232 protocol group In summary, the traditional telephone network transmits voice in a circuit-switched manner, and the required transmission bandwidth is 64 kbit/s. In order to make full use of network bandwidth resources, VoIP communication usually uses various compression algorithms to compress the original voice data according to actual requirements. Commonly used are G.723.1, G.729, etc.; then network technology will compress After the voice data is packaged, the connection layer uses UDP in the transport layer. The main purpose is to ensure the real-time transmission of voice data, and then the UDP data is transmitted to the IP packet network for transmission; Before the data is transmitted to UDP, the compressed data is processed by the RTP/RTCP protocol, the RTP protocol is used to transmit the voice data, and the RTCP protocol is used to transmit the control information of the voice data. As shown on the left side of Figure 4. After the receiving side receives the data, its processing is reversed from the transmitting side, as shown on the right side of Figure 4. Figure 4 Schematic diagram of voice data processing Usually, each gateway needs to send both voice data and voice data, so it contains all the functions in Figure 3. In fact, the basic function of the gateway is to complete the compression, decompression, packing and unpacking of voice data. The actual transmission network may be a very simple local area network, or an extremely complex wide area network. The transmission path includes various network devices, such as network switches, routers, ATM switches, SDH, and the like. 2.2 Main protocol set In many cases, VoIP technology only refers to the ability to implement a similar old-fashioned phone over an IP network. However, in the case of the continuous development of the traditional telephone network business, the meaning and design goals of VoIP also exceed its literal meaning; that is to say, VoIP technology not only refers to the traditional telephone technology that provides the conversation between the two parties, but also contains voice, image and data. Supporting both parties and multi-party multimedia communication technologies for various intelligent services. VoIP media coding technologies include the popular G.723.1, G.729, G.729A voice compression coding algorithms and MPEG-II multimedia compression technology. There are still many coding technologies. For details, please refer to the introduction in Section 4. Control signaling technology involved in VoIP: including two sets of standard systems, ITU-T H.323 and IETF Session Initiation Protocol SIP [4] (Session InitaTIon Protocol), and also involves real-time streaming protocol for real-time synchronous continuous media stream transmission control. TRSP. At the same time, it also supplements the MGCP protocol, that is, the MGCP protocol is actually a supplementary agreement. The gateway device in the H.323 protocol and the SIP protocol not only performs media format conversion, such as compression and decompression, RTP packing and unpacking, but also performs signaling conversion, and performs H. on the IP network side. 323 or SIP protocol, performing circuit switched signaling on the PSTN side. In this way, the function of the gateway becomes very complicated, which limits the capacity of each gateway device; moreover, as the application becomes more and more popular, more gateway terminals will enter the user, and such gateway devices have higher costs and exist in the network. Security and other issues seriously affect the application of VoIP systems. The MGCP protocol can solve these problems. The basic idea is to separate the media transformation function from the gateway control function. The gateway is only responsible for a simple media conversion function called Media Gateway (MG: Media Gateway). The complex gateway control function is performed by an independent control entity outside the gateway. This entity is called Call Agent (CA: Call Agent). ), the interface between the two uses the MGCP protocol to interact. Packet transmission technology involved in VoIP: mainly uses the real-time transport protocol RTP. The service quality assurance technologies involved in VoIP include the resource reservation protocol RSVP, the quality of service QoS, and the real-time transmission control protocol RTCP for service quality monitoring to avoid network congestion and guarantee call quality. The network transmission technologies involved in VoIP are mainly TCP and UDP. In addition, it involves packet reconstruction technology and delay jitter smoothing technology, dynamic route balanced transmission technology, gateway interconnection technology (including media interworking and control signaling interworking), network management technology (SNMP), security authentication and charging technology, and IVR interaction. Voice response technology and more. 2.3 Technical characteristics VoIP applications have developed rapidly in recent years and are inseparable from many of their unique technical features. The main features are: 1. low cost Low prices have been a very important factor in the development of VoIP technology. VoIP will use voice compression technology. Although it adds RTP/UDP/IP encapsulation and the overhead of the underlying transmission, it usually only needs 1/3~1/4 of the bandwidth of traditional circuit switching. Moreover, using VoIP technology to transmit voice, In essence, it is packet statistical multiplexing, so that the utilization of network bandwidth can be improved to a greater extent. At the same time, with the rapid development of VoIP technology, the production costs of gateways and other devices have also dropped rapidly. Low cost has laid a solid foundation for the rapid deployment of VoIP technology. 2. Easy to implement value-added services The advantage of VoIP technology is not only the low price, but also the flexible implementation of value-added services is the real driving force for the development of VoIP. VoIP uses intelligent terminals, and the IP network is an open network. Its inherent distributed computer environment can easily introduce new services quickly. Relatively speaking, the introduction of a value-added service by the telephone network is often difficult, sometimes limited by terminal capabilities and network interoperability, and some services are not yet available. In the central office system, the traditional telephone network uses intelligent network technology to realize value-added services, and VoIP technology is inherently more flexible and intelligent than the intelligent network technology. The figure below is a comparison of traditional PSTN networks and VoIP. It can be clearly seen from Figure 5 that VoIP has obvious advantages in terms of call cost, and the call quality is slightly inferior, but it is constantly developing and strengthening. Therefore, VoIP services have brought huge impacts to the traditional communications industry, and also brought business opportunities to emerging operators. Figure 5 Comparison of traditional and VoIP phone technologies
Terminals refer to terminal Connectors,which are divided into single holes,double holes,sockets, hooks etc.From materials:copper plating, copper galvanizing, copper,aluminum,iron,etc.Their role is mainly to transmit electrical signals or to conduct electricity.
Our company's Terminal Connectors are divided into these series(as follow),which are hot-selling in recent few years:
Copper Tube Connectors(GTY)
Terminal Connectors,Sc Cable Lug,Cable Lug,Terminal Lug Ningbo Bond Industrial Electric Co., Ltd. , https://www.bondelectro.com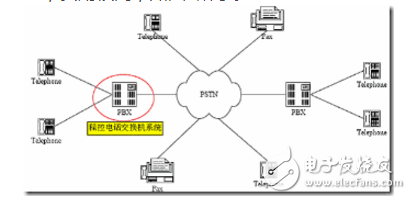
JGK End Junction Terminal Connectors
JGA End Junction Terminal Connectors
JGY End Junction Terminal Connectors
JGB End Junction Terminal Connectors
DTL-1 Aluminium-Copper Terminal Connector
DTL-2 Aluminium-Copper Terminal Connector
DT Copper End Junction Terminals
DL Aluminium End Junction Terminals
Bus-Bar Terminal Connector
SM Insulate Terminal Connectors
One hole long barrel copper lugs
Two holes long barrel copper lugs