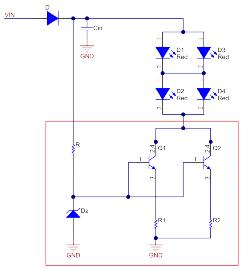
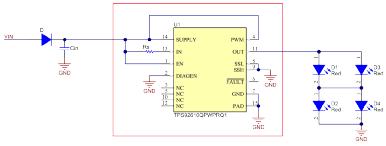
This article refers to the address: http:// CHMSL stands for the central high-position brake light and is mounted above the left and right brake lights (also known as brake lights) on the right side of the vehicle. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, when the brake system is working, CHMSL should provide clear and accurate information to the rear driver, telling them that they must slow down. Since the CHMSL is installed outside the left and right brake lights, it is also called the "third brake light". In addition to the brake light function, some vehicles (such as pickup trucks) also have a backup light integrated in the CHMSL. Install applications using discrete components of CHMSL In modern vehicles, the internal illumination of CHSMSL is based primarily on light-emitting diode (LED) strings. A transistor circuit is used to drive the LED string in CHMSL. In contrast to switching circuits, the CHMSL LED driver circuit is typically a linear circuit; that is, the LED is driven by a circuit in which the transistor operates in its linear region. Designers typically use discrete resistors and low-side bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) to implement discrete component-based LED driver circuits in the CHMSL module. Figure 1 shows an example of a discrete LED driver circuit for CHMSL. In this circuit, CHMSL consists of two LED strings, each of which is built on top of two red LEDs in series. The BJT is located on the underside of the LED. Heat dissipation considerations Thermal performance must be considered when designing a linear LED driver circuit. Circuit design and component selection must ensure that the component does not reach the temperature point that caused the damage. According to the schematic of Figure 1, you can see that as the supply voltage increases, the voltage across the BJT and the resistor increases, increasing the power consumption of these components. More power consumption means higher temperatures. Therefore, in linear LED driver applications, controlling the input voltage range helps solve most of the thermal issues. To analyze the heat dissipation problem of the schematic in Figure 1, consider an example where the total current of the CHMSL LED is 90mA, so each LED string is driven at 45mA. Using the 16V supply voltage, the maximum voltage drop across the BJT is calculated from Equation 1 to be 9V: Equation 2 calculates the maximum power consumption of the BJT to be 0.81W: Assuming a maximum operating ambient temperature of 85 ° C and a BJT in a small outline transistor (SOT)-223 package with a thermal resistance of 80 ° C / W, the maximum BJT junction temperature calculated by Equation 3 is: This calculation indicates that the junction temperature is very close to the standard maximum allowable junction temperature of 150 °C. In order to improve the heat dissipation performance of the circuit, two parallel transistors are used to dissipate the power consumption. Even in the worst case, the maximum temperature can be kept below 150 °C, as shown in Equation 4: When using different BJT package types with higher thermal resistance, more BJTs are needed to allocate power. The number and size of shunt transistors is based primarily on the LED current and the maximum power dissipation allowed by the transistor. CHMSL installation application with integrated LED driver IC Another way to drive LEDs is to use a specific linear LED driver integrated circuit (IC), such as Texas Instruments' TPS92610-Q1, as shown in Figure 2. In this IC driver, both the transistor and the transistor driver circuit are integrated within the IC. The transistor still operates in its linear region. Since all components are integrated inside the IC, you only need an IC and a sense resistor to implement this solution. Figure 2: TPS92610-Q1 integrated LED driver circuit Consider heat dissipation again Let's take a look at the heat dissipation issues in this design. Specifically, it is the junction temperature of the IC. At 16V supply voltage, Equation 5 calculates the maximum voltage drop on the IC to be 11V: Assuming the IC has the same 90mA current, the maximum voltage drop across the IC is 11V and the thermal resistance is 52°C / W, then Equation 6 calculates the maximum junction temperature: 136.5 ° C is well below the maximum specified IC junction temperature of 150 ° C. Therefore, you only need one driver IC to operate the CHMSL LED string in the example. The advantages of an integrated solution A clear advantage of an integrated solution is the reduced number of components compared to a discrete solution. Reducing the number of components on the board will significantly reduce space requirements. Another key advantage is the accuracy of current regulation over the entire temperature range. As the forward voltage of the LED changes with temperature, the driver IC can keep the current in the IC constant. This is in contrast to the discrete circuit shown in Figure 1, which does not regulate the current in the LED as the temperature changes. A third advantage of the linear LED driver IC solution is its diagnostics, which can detect LED circuit faults such as LED open and short circuits and notify the driver of the fault. Finally, the application shown in Figure 2 may be less expensive than in Figure 1 when considering the number of components and the cost of each component. Power Station 600W,Outdoor Mobile Power Station,Portable Power Bank,Mobile Power Bank Guangdong pisen electronics co., ltd , https://www.pisenpro.com

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()